Vaginal Dryness During Menopause
Meta Description: Understand why vaginal dryness during menopause occurs and explore effective treatments, from moisturizing therapies to low-dose estrogen and laser [...]
Read MoreAppendicitis pain typically starts near the navel and migrates to McBurney's point (one-third the distance from hip bone to navel) within 12-24 hours, often worsening with coughing or walking.
Ovarian torsion requires surgical intervention within 6 hours to save the ovary, with peak occurrence in women aged 20-30 and those with ovarian cysts larger than 5 centimeters.
Kidney stones cause severe, colicky pain that radiates from back to groin, with 90% of stones smaller than 5mm passing naturally within 4-6 weeks through increased fluid intake.
Crohn's disease affects the terminal ileum in 80% of cases, causing chronic inflammation that can lead to strictures, abscesses, and requires different treatment than acute appendicitis.
CT scans have 95% accuracy for appendicitis diagnosis, while transvaginal ultrasound is preferred for suspected ovarian pathology in women of reproductive age.
Right lower quadrant abdominal pain is a common complaint that can stem from various underlying conditions. The right lower quadrant (RLQ) of the abdomen houses several vital organs, including parts of the intestines, the appendix, and in women, the ovaries and fallopian tubes. Understanding the potential causes of right lower quadrant pain in this area is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment.
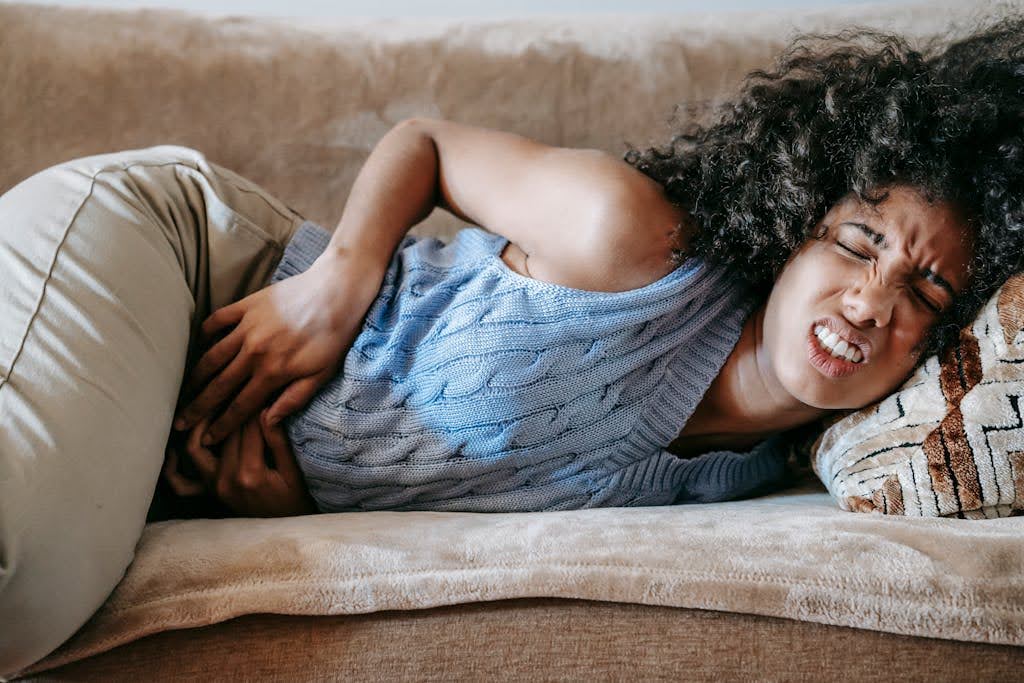 Common Causes of Right Lower Quadrant Pain
Common Causes of Right Lower Quadrant PainAppendicitis is one of the most well-known causes of right lower quadrant pain. It occurs when the appendix becomes inflamed, often due to a blockage. Symptoms typically include sharp pain that starts around the navel and then shifts to the RLQ, along with fever, nausea, and vomiting.
If left untreated, appendicitis can lead to serious complications, such as a ruptured appendix, which can result in peritonitis—a life-threatening infection of the abdominal cavity. Immediate medical attention is essential in such cases. The standard treatment for appendicitis is an appendectomy, a surgical procedure to remove the inflamed appendix. Recovery time varies, but many patients can return to normal activities within a few weeks, provided there are no complications.
In women, right lower quadrant pain may be associated with ovarian conditions, such as ovarian cysts or torsion. Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can develop on the ovaries and may cause discomfort, especially if they rupture. Symptoms can include sharp or dull pain, irregular menstrual cycles, and bloating.
Ovarian torsion, which occurs when an ovary twists around the ligaments that hold it in place, is a medical emergency that requires immediate intervention. Symptoms often include sudden, severe pain and may be accompanied by nausea or vomiting. If diagnosed promptly, surgical intervention can often save the affected ovary, but delayed treatment can lead to loss of the ovary and other complications. Regular gynecological check-ups can help monitor ovarian health and detect issues early.
Various gastrointestinal disorders can also lead to pain in the right lower quadrant. Conditions such as Crohn's disease, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and diverticulitis can manifest with RLQ pain. Crohn's disease, an inflammatory bowel condition, may cause abdominal pain, diarrhea, and weight loss. This chronic condition can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract and may lead to serious complications, including strictures and fistulas, which may require surgical intervention.
Diverticulitis, which involves inflammation of diverticula (small pouches that can form in the colon), can lead to localized pain, fever, and changes in bowel habits. It is essential to differentiate between these conditions to provide appropriate treatment. Dietary modifications, such as increasing fiber intake, can help manage diverticulitis and prevent flare-ups. Additionally, understanding the triggers for IBS can empower patients to make lifestyle changes that alleviate their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
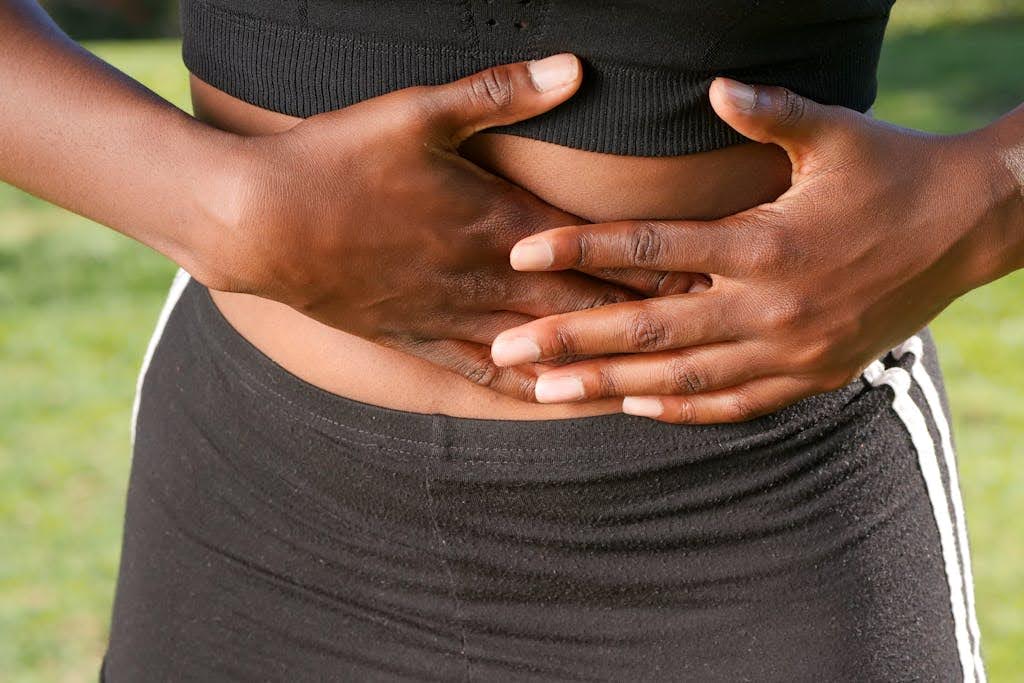 Kidney Stones
Kidney StonesKidney stones can cause significant pain that may radiate to the right lower quadrant. The pain is typically severe and can come in waves as the stone moves through the urinary tract. Other symptoms may include blood in the urine, nausea, and frequent urination.
Diagnosis usually involves imaging studies, such as a CT scan, and treatment may range from pain management to surgical intervention, depending on the size and location of the stone. It's important to note that hydration plays a crucial role in both the prevention and management of kidney stones. Drinking plenty of fluids can help dilute the substances in urine that lead to stone formation. Additionally, dietary adjustments, such as reducing sodium intake and avoiding excessive oxalate-rich foods, can also be beneficial for those prone to developing stones.
A hernia occurs when an organ or tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal wall. Inguinal hernias, which can occur in the groin area, may present with pain in the right lower quadrant. Symptoms can include a noticeable bulge and discomfort that worsens with activity or straining.
Treatment often involves surgical repair, especially if the hernia is incarcerated or strangulated, which can lead to serious complications. It's also worth mentioning that certain lifestyle factors, such as obesity, chronic coughing, or heavy lifting, can increase the risk of developing a hernia. Preventative measures, including maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in core-strengthening exercises, can help reduce the likelihood of hernia formation.
Pain in the right lower quadrant may also arise from musculoskeletal issues, such as muscle strains or ligament injuries. Activities that involve heavy lifting or sudden movements can lead to strains that cause localized pain in the abdomen.
These types of pain are typically less severe than those caused by internal conditions and may improve with rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain relief. However, it's important to differentiate between musculoskeletal pain and pain stemming from internal organs, as the latter may require more immediate medical attention. Physical therapy can be an effective treatment option for musculoskeletal pain, helping to strengthen the affected area and prevent future injuries. Additionally, incorporating regular stretching and strengthening exercises into one’s routine can enhance overall flexibility and resilience, potentially reducing the risk of such injuries in the future.
Recognizing accompanying symptoms can aid in identifying the underlying cause of right lower quadrant pain. Some common symptoms to watch for include:
Fever and chills
Nausea and vomiting
Changes in bowel habits (diarrhea or constipation)
Abdominal swelling or bloating
Urinary symptoms (painful urination, blood in urine)
Each of these symptoms can provide important clues regarding the nature of the pain and the urgency of medical evaluation. For instance, the presence of fever and chills often suggests an infectious process, such as appendicitis or diverticulitis, which may require prompt surgical intervention. Similarly, nausea and vomiting can indicate gastrointestinal obstruction or inflammation, necessitating further diagnostic imaging to ascertain the underlying issue.
Moreover, changes in bowel habits, whether they manifest as diarrhea or constipation, can point towards conditions like irritable bowel syndrome or inflammatory bowel disease. Abdominal swelling or bloating may indicate fluid accumulation or gas buildup, which can be associated with various gastrointestinal disorders. Lastly, urinary symptoms, including painful urination or hematuria (blood in urine), may suggest a urinary tract infection or kidney stones, both of which can present with right lower quadrant discomfort. Understanding these symptoms in conjunction with the pain can significantly enhance the diagnostic process and guide appropriate treatment strategies.
 It is crucial to understand when to seek medical attention for right lower quadrant pain. Certain warning signs indicate that immediate evaluation is necessary:
It is crucial to understand when to seek medical attention for right lower quadrant pain. Certain warning signs indicate that immediate evaluation is necessary:
Severe or worsening pain
Signs of infection (fever, chills)
Persistent vomiting
Inability to pass gas or have a bowel movement
Blood in urine or stool
Prompt medical evaluation can be life-saving, especially in cases of appendicitis, ovarian torsion, or other serious conditions. It’s important to note that right lower quadrant pain can stem from a variety of causes, ranging from benign to life-threatening. For instance, conditions such as diverticulitis or kidney stones can also present with similar symptoms, necessitating a thorough examination by a healthcare professional.
In addition to the aforementioned symptoms, individuals should be aware of accompanying signs that may warrant immediate medical attention. These can include unexplained weight loss, changes in appetite, or a sudden onset of pain that feels different from any previous episodes. Understanding your body and recognizing these changes can empower you to seek help sooner rather than later, potentially preventing complications and ensuring a more favorable outcome.
To determine the cause of right lower quadrant pain, healthcare providers typically employ a variety of diagnostic methods. These may include:
A thorough physical examination is often the first step. The healthcare provider will assess the abdomen for tenderness, swelling, and other abnormalities. They may also inquire about the patient's medical history and any accompanying symptoms. For instance, the provider might ask about the onset, duration, and nature of the pain, as well as any changes in bowel habits or urinary function. This information can provide crucial insights into potential underlying conditions, guiding further diagnostic steps.
Imaging studies play a critical role in diagnosing the cause of abdominal pain. Common modalities include:
Ultrasound: Particularly useful for evaluating ovarian issues and gallbladder disease. It is a non-invasive procedure that uses sound waves to create images, allowing for real-time assessment of the organs.
CT Scan: Provides detailed images of the abdominal organs and is often used to diagnose appendicitis or kidney stones. CT scans can also help identify other conditions such as diverticulitis or tumors, making it a versatile tool in abdominal diagnostics.
X-rays: May be used to identify bowel obstructions or other structural issues. While less commonly used for soft tissue evaluation, X-rays can still provide valuable information about the presence of air-fluid levels in the intestines.
Laboratory tests can help identify infections or other underlying conditions. Blood tests may reveal signs of inflammation or infection, while urinalysis can help diagnose urinary tract issues. Additionally, specific markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) levels can indicate the presence of inflammatory processes in the body. In some cases, stool tests may also be conducted to check for infections or blood, providing further clues to the underlying cause of abdominal discomfort.
Furthermore, in cases where appendicitis is suspected, healthcare providers may utilize a combination of these diagnostic tools to confirm their suspicions. For example, a patient presenting with severe right lower quadrant pain, fever, and elevated white blood cell count may be quickly referred for a CT scan to visualize the appendix. This multi-faceted approach not only enhances diagnostic accuracy but also aids in the timely management of potentially serious conditions, ensuring that patients receive appropriate care without unnecessary delays.
Treatment for right lower quadrant pain depends on the underlying cause. Here are some common approaches:
 Medications
MedicationsFor conditions such as infections or inflammatory diseases, medications may be prescribed. Antibiotics are often used for bacterial infections, while anti-inflammatory drugs can help reduce pain and swelling. In addition to these, analgesics may be recommended to manage pain effectively, allowing patients to carry out daily activities with minimal discomfort. In some cases, medications that target specific conditions, such as antispasmodics for gastrointestinal issues, can also be beneficial in alleviating symptoms.
In cases where conditions like appendicitis, ovarian torsion, or hernias are diagnosed, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgery can provide definitive treatment and prevent complications. Laparoscopic techniques are increasingly popular due to their minimally invasive nature, which often results in shorter recovery times and reduced postoperative pain. Furthermore, timely surgical intervention can be crucial in preventing more serious complications, such as rupture or severe infection, which can pose significant health risks.
For less severe conditions, conservative management may be appropriate. This can include rest, dietary modifications, and over-the-counter pain relief. Monitoring symptoms is essential to ensure they do not worsen. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as increased hydration, regular physical activity, and stress management techniques can play a vital role in managing chronic pain. Patients are often encouraged to keep a symptom diary, which can help healthcare providers tailor treatment plans more effectively by identifying triggers and patterns associated with the pain.
While not all causes of right lower quadrant pain can be prevented, certain lifestyle choices can help reduce risk factors:
Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fiber can promote digestive health and reduce the risk of gastrointestinal issues. Staying hydrated is also essential for kidney health. Incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can enhance nutrient intake and support overall bodily functions. Foods high in antioxidants, such as berries and leafy greens, can also help combat inflammation, which is crucial for preventing conditions that may lead to abdominal pain.
Engaging in regular physical activity can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of conditions such as hernias and diverticulitis. Activities like walking, swimming, or cycling not only improve cardiovascular health but also promote better digestion and can alleviate stress, which is known to exacerbate gastrointestinal discomfort. Additionally, strength training can enhance core stability, potentially reducing the risk of injury to the abdominal area.
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help identify potential health issues early, allowing for timely intervention. This is especially important for individuals with a family history of abdominal conditions. During these visits, discussing any changes in symptoms or new concerns can lead to more tailored preventive strategies. Moreover, screenings for conditions such as colon cancer or inflammatory bowel disease can be crucial in catching issues before they develop into more serious problems.
Pain in the right lower quadrant of the abdomen can stem from a range of issues—some minor, others more serious. With Doctronic, identifying potential causes, spotting warning signs, and knowing when to seek help becomes easier and more accessible. By turning to reliable insights and timely guidance, you can take informed steps toward relief and long-term health.
Severe or worsening pain with fever above 101°F, persistent vomiting, or inability to pass gas requires immediate emergency evaluation to rule out surgical emergencies. Early diagnosis within the first 24 hours significantly improves outcomes and reduces complications. If you're experiencing concerning symptoms, Doctronic can help you understand when to seek immediate care.
Meta Description: Understand why vaginal dryness during menopause occurs and explore effective treatments, from moisturizing therapies to low-dose estrogen and laser [...]
Read MoreMeta Description: Discover why perimenopause causes itching and explore effective relief strategies, from hormone therapy to skincare tips, to soothe dry and itchy skin.When [...]
Read MoreMeta Description: Understand why weight gain during perimenopause occurs and learn how to manage it through protein intake, resistance training, and better sleep habits.Why [...]
Read More