Skin conditions can be perplexing, especially when symptoms overlap. Two common conditions that often cause confusion are scabies and eczema. Both can lead to discomfort, itching, and inflammation, but they have distinct causes and treatments. Understanding the differences between scabies and eczema is crucial for effective management and relief.
 Understanding Scabies
Understanding Scabies
Scabies is a contagious skin infestation caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite. This microscopic parasite burrows into the skin, leading to intense itching and a rash. Scabies is highly contagious and can spread through direct skin-to-skin contact, making it essential to identify and treat the condition promptly. The mite can survive for up to 72 hours off the human body, which means that even inanimate objects like bedding, clothing, and towels can harbor the mites, posing a risk for transmission. This aspect of scabies transmission underscores the importance of thorough cleaning and disinfection in addition to medical treatment.
Symptoms of Scabies
The primary symptom of scabies is intense itching, which often worsens at night. Other symptoms may include:
Itching is caused by an allergic reaction to the mites, their eggs, and their waste. The rash typically appears in areas where the mites burrow, such as between the fingers, on the wrists, elbows, and buttocks. In some instances, the rash can spread to other parts of the body, leading to secondary bacterial infections due to scratching. This can complicate the condition, making prompt treatment even more critical. Additionally, individuals with weakened immune systems or those who are elderly may experience more severe symptoms and complications, highlighting the need for vigilance in at-risk populations.
How Scabies is Diagnosed
Diagnosis usually involves a physical examination by a healthcare provider. They may look for characteristic signs of scabies, such as burrows or rashes. In some cases, a skin scraping may be taken to confirm the presence of mites under a microscope. Healthcare providers may also consider the patient's history and symptoms, as well as the possibility of scabies outbreaks in the community, which can aid in making an accurate diagnosis. In certain situations, a dermatoscope may be used to enhance the visualization of the mite burrows, providing further confirmation of the infestation.
Treatment Options for Scabies
Treatment for scabies typically involves prescription topical medications, such as permethrin cream or ivermectin. These treatments are designed to kill the mites and alleviate symptoms. It is crucial to treat all close contacts simultaneously to prevent reinfestation. In addition to topical treatments, oral medications may be prescribed in cases of crusted scabies, which is a more severe form of the infestation characterized by thick, crusted lesions that can harbor thousands of mites. After treatment, it is advisable to wash all clothing, bedding, and towels in hot water and dry them on a hot cycle to eliminate any remaining mites and eggs, ensuring a comprehensive approach to eradication.
Understanding Eczema
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. Unlike scabies, eczema is not contagious and is often associated with other allergic conditions, such as asthma and hay fever. The exact cause of eczema is not fully understood, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Individuals with a family history of eczema or other allergic conditions are at a higher risk of developing this skin disorder, highlighting the importance of understanding one’s genetic background when assessing skin health.
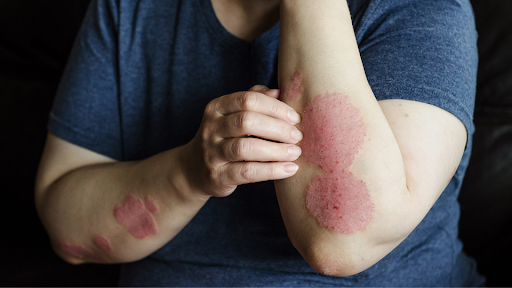 Symptoms of Eczema
Symptoms of Eczema
Symptoms of eczema can vary widely from person to person, but they typically include:
Dry, sensitive skin
Intense itching, which may worsen at night
Red or brownish-gray patches, often found on the hands, feet, ankles, wrists, neck, upper chest, eyelids, inside the bend of the elbows and knees
In some cases, eczema can lead to thickened, cracked skin or small, raised bumps that may leak fluid when scratched. These symptoms can be exacerbated by environmental factors such as weather changes, irritants like soaps and detergents, and stress. Understanding these triggers is crucial for effective management, as avoiding them can significantly reduce flare-ups and improve overall skin condition. Moreover, the psychological impact of eczema should not be overlooked; many individuals experience anxiety or social withdrawal due to the visible nature of their symptoms.
How Eczema is Diagnosed
Diagnosis of eczema involves a thorough medical history and physical examination. A healthcare provider will assess the pattern of the rash and may inquire about family history and any known allergies. In some instances, patch testing may be performed to identify specific allergens that may be triggering the condition. Additionally, a provider may recommend keeping a symptom diary to track flare-ups and potential triggers, which can provide valuable insights into the individual's unique experience with eczema.
Treatment Options for Eczema
While there is no cure for eczema, various treatments can help manage symptoms. These include:
Moisturizers to hydrate the skin
Topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
Antihistamines to alleviate itching
For more severe cases, systemic medications or phototherapy may be recommended. It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan. In addition to these medical treatments, lifestyle modifications such as adopting a gentle skincare routine, wearing breathable fabrics, and maintaining a balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids may also contribute to improved skin health. Furthermore, support groups and counseling can provide emotional relief and practical advice for those coping with the challenges of living with eczema, fostering a sense of community and shared experience among individuals facing similar struggles.
Key Differences Between Scabies and Eczema
While scabies and eczema can present similar symptoms, key differences can help distinguish between the two conditions. Understanding these differences is vital for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Causes
A parasitic infestation causes scabies, while eczema is primarily a result of genetic and environmental factors. Eczema often has an allergic component, whereas scabies is purely infectious. The mites responsible for scabies, known as Sarcoptes scabiei, burrow into the skin, leading to intense itching and inflammation. In contrast, eczema can be triggered by a variety of factors, including allergens like pollen, dust mites, and certain foods, as well as irritants such as soaps and fabrics. This multifactorial nature of eczema means that individuals may need to identify and avoid specific triggers to manage their symptoms effectively.
Transmission
Scabies is highly contagious and can spread through close contact with an infected person. In contrast, eczema is not contagious and cannot be transmitted from person to person. The contagious nature of scabies makes it particularly concerning in communal living situations, such as nursing homes or schools, where close physical contact is common. This necessitates prompt treatment not only for the infected individual but also for close contacts to prevent further outbreaks. On the other hand, eczema’s non-contagious nature allows individuals to interact freely without the fear of spreading the condition, although they may still experience social stigma due to the visible symptoms.
Appearance of the Rash
The rash associated with scabies typically features burrows and is often found in specific areas of the body, whereas eczema can appear as dry, flaky patches that may occur anywhere on the body. Scabies rashes often manifest between the fingers, on the wrists, and in the folds of the skin, presenting as small red bumps or blisters that can become infected if scratched. Eczema, however, tends to be more widespread and can vary in appearance from person to person, sometimes resembling red, inflamed patches or even crusty lesions. The chronic nature of eczema can lead to thickened skin over time, a condition known as lichenification, which can further complicate the management of the disease. Understanding these distinct characteristics is crucial for healthcare providers to recommend appropriate treatments and interventions tailored to each condition.
When to Seek Medical Advice
It is essential to consult a healthcare provider if experiencing persistent skin issues. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and provide relief. If there is uncertainty about whether the symptoms are due to scabies or eczema, professional evaluation is crucial. Skin conditions can often be indicative of underlying health issues, and timely intervention can lead to better outcomes. For instance, untreated eczema can lead to skin infections, while scabies can spread to others if not addressed promptly. Therefore, recognizing the importance of professional guidance cannot be overstated.
Using Telehealth for Skin Conditions
For those who may not have immediate access to a healthcare provider, telehealth services can be a convenient option. Platforms like Doctronic.ai offer affordable telehealth visits with licensed doctors available 24/7 across all 50 states. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals seeking quick answers about their skin conditions. Telehealth not only saves time but also reduces the stress of traveling to a clinic, especially for those with mobility issues or busy schedules. Additionally, many telehealth services provide follow-up consultations, allowing for continuous monitoring of the condition without the need for in-person visits.
What to Expect During a Consultation
During a telehealth consultation, patients can expect to discuss their symptoms in detail. Healthcare providers may ask about the onset of symptoms, any known allergies, and previous treatments. They may also request photos of the affected areas to facilitate diagnosis. This visual aid can be incredibly helpful in assessing the severity and nature of the skin condition. Furthermore, patients should be prepared to share information about their lifestyle, such as skincare routines, exposure to irritants, and stress levels, as these factors can significantly influence skin health. The consultation aims to create a comprehensive understanding of the patient's situation, enabling the provider to recommend the most effective treatment options tailored to individual needs.
Self-Care and Management Strategies
Whether dealing with scabies or eczema, self-care plays a crucial role in managing symptoms and promoting skin health. Here are some strategies to consider:
For Scabies
Follow treatment recommendations carefully and treat all close contacts.
Wash bedding and clothing in hot water to eliminate mites.
Avoid scratching to prevent secondary infections.
In addition to these strategies, it’s important to maintain a clean living environment to help prevent reinfestation. Regular vacuuming of carpets and upholstered furniture can significantly reduce the presence of mites. Consider using a steam cleaner for a deeper clean, especially in areas where pets may frequent. Furthermore, educating yourself about the life cycle of scabies can empower you to take proactive measures, such as avoiding close skin-to-skin contact with infected individuals until they have completed their treatment. This knowledge not only aids in your own recovery but also helps in preventing the spread of infestation to others.
For Eczema
Apply moisturizers regularly to keep the skin hydrated.
Identify and avoid triggers, such as certain fabrics or allergens.
Practice stress management techniques, as stress can exacerbate symptoms.
Moreover, incorporating a gentle skincare routine can make a significant difference in managing eczema. Opt for fragrance-free and hypoallergenic products to minimize irritation. When bathing, use lukewarm water instead of hot, as hot water can strip the skin of its natural oils. After bathing, apply a thick layer of moisturizer while the skin is still damp to lock in moisture effectively. Additionally, consider keeping a symptom diary to track flare-ups and identify patterns related to diet, weather changes, or stress levels. This can provide valuable insights into your condition and help you make informed decisions about lifestyle adjustments that may alleviate symptoms.
Targeted Care for Skin Relief
Understanding the differences between scabies and eczema is essential for effective management and treatment. While both conditions can cause discomfort and distress, they require different approaches to care. If experiencing skin issues, consider utilizing telehealth services like Doctronic.ai for quick access to medical advice and support.
By recognizing the symptoms and seeking timely treatment, individuals can find relief and improve their skin health. Whether it’s through traditional methods or innovative telehealth solutions, effective care is within reach.
Experience the Future of Personalized Care with Doctronic
Don't let the uncertainty of skin conditions like scabies and eczema slow you down. With Doctronic, you're just seconds away from a free AI doctor visit that leverages the most current, peer-reviewed medical research to address your concerns. Our AI doctor is designed to provide personalized, attentive care without the wait, remembering every detail of your health history for a truly individualized experience. For added convenience, you can also opt for an affordable telehealth video visit with our doctors anytime, anywhere. Join over 10 million satisfied users and skip the line to talk to an AI Doctor now, for free.



 Understanding Scabies
Understanding Scabies Symptoms of Eczema
Symptoms of Eczema