Can Pain in Your Back Cause Chest Discomfort?
Experiencing chest discomfort can be alarming, often prompting thoughts of heart-related issues. However, the source of chest pain is not always cardiac in nature. One common [...]
Read More
Medically reviewed by Alan Lucks | MD, Alan Lucks MDPC Private Practice - New York on October 12th, 2025.
Referred pain occurs when irritated nerves in the T1-T12 thoracic vertebrae send signals that the brain misinterprets as originating from the chest wall or ribcage area.
Herniated thoracic discs affect only 1% of all spinal disc herniations but commonly cause chest pain that wraps around the ribcage in a band-like pattern.
Upper back muscle strain creates chest wall tightness that characteristically worsens with deep breathing, coughing, or twisting movements—unlike cardiac pain which occurs at rest.
Musculoskeletal chest pain improves within 2-6 weeks with conservative treatment, while cardiac chest pain requires immediate intervention and doesn't respond to position changes.
Red flag symptoms requiring emergency care include chest pain with diaphoresis, nausea, left arm radiation, or pain that occurs during minimal exertion rather than movement.
Experiencing chest discomfort can be alarming, often prompting thoughts of heart-related issues. However, the source of chest pain is not always cardiac in nature. One common but less recognized cause is pain originating from the back. Understanding the relationship between back pain and chest discomfort is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. This article explores how back pain can lead to chest discomfort, the underlying causes, and when to seek medical attention.
Chest discomfort is a broad term that encompasses a variety of sensations, including sharp pain, pressure, tightness, or burning. While heart problems are a critical cause to rule out, other sources, such as musculoskeletal issues, can also produce similar symptoms. The back and chest are anatomically connected through muscles, nerves, and the rib cage, which means pain in one area can sometimes be felt in the other.
Back pain that causes chest discomfort often stems from issues involving the thoracic spine, which is the middle section of the spine attached to the ribs. Problems in this area can irritate nerves or muscles, leading to referred pain that manifests as chest discomfort. This phenomenon is known as referred pain, where the brain interprets pain signals from one part of the body as coming from another.
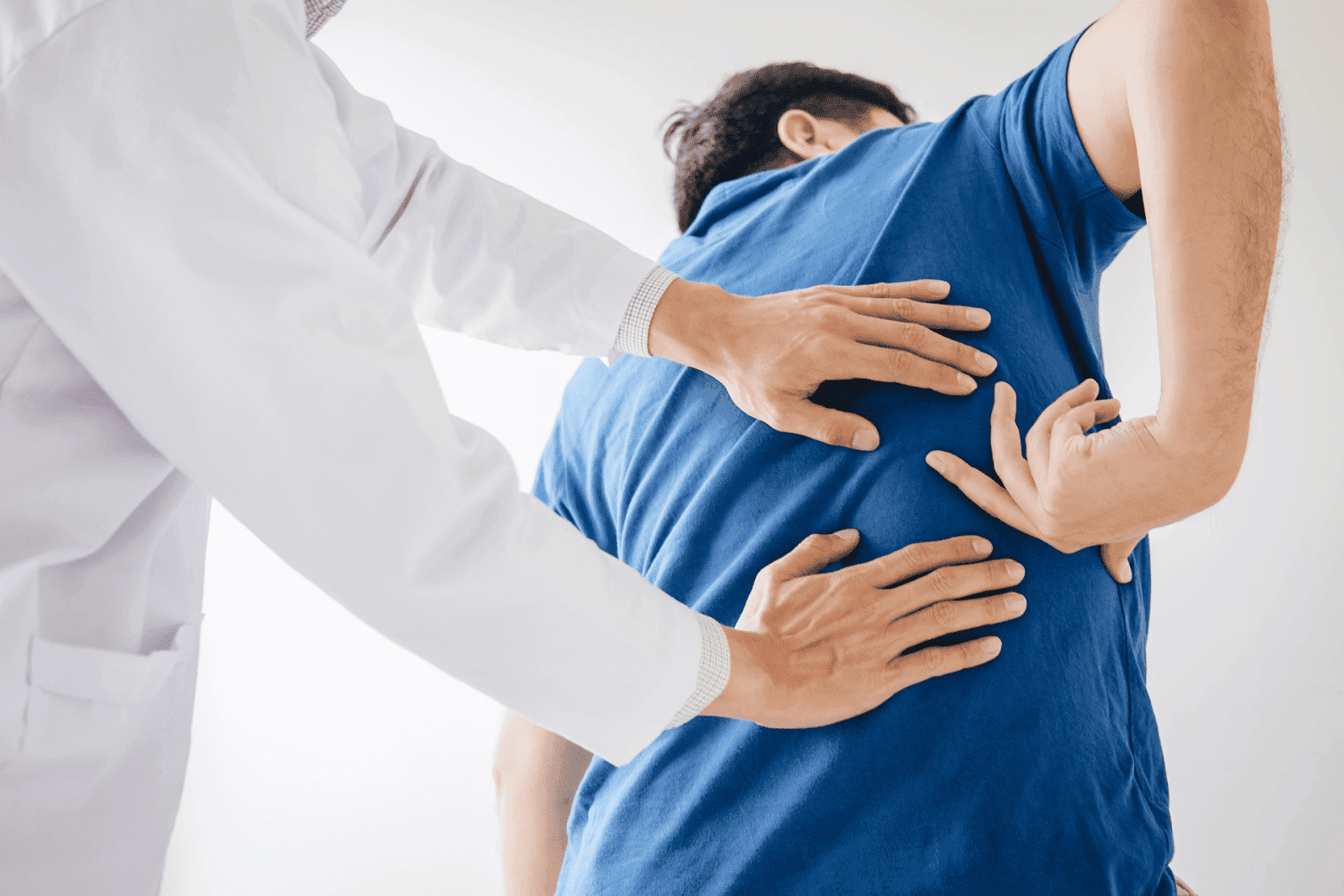 How Nerve Irritation Can Cause Chest Pain
How Nerve Irritation Can Cause Chest PainThe thoracic spine contains nerves that branch out to the chest wall and abdomen. When these nerves are compressed or inflamed due to spinal issues such as herniated discs, arthritis, or muscle strain, the pain signals can travel along the nerve pathways and present as chest pain. For example, a pinched nerve in the upper back may cause sharp, shooting pain that radiates around the ribs to the front of the chest.
This type of pain can mimic cardiac chest pain, which is why it is important to differentiate between the two. Unlike heart-related pain, nerve-related chest discomfort often worsens with certain movements or positions and may be accompanied by back stiffness or tenderness. Additionally, patients may experience sensations such as tingling or numbness in the arms or shoulders, further indicating that the source of the discomfort is likely linked to nerve irritation rather than cardiac issues.
Muscle strain in the upper back or chest wall can also cause chest discomfort. Activities such as heavy lifting, poor posture, or sudden movements can strain muscles attached to the ribs and spine. This strain can lead to inflammation and localized pain that feels like it is coming from the chest.
Muscle-related chest pain is typically sharp or aching and may increase with deep breathing, coughing, or physical activity. Unlike cardiac pain, it usually improves with rest and over-the-counter pain relievers. Furthermore, muscle strains can be exacerbated by stress, as tension in the upper body can lead to tightness and discomfort. Stretching and strengthening exercises, along with ergonomically designed workspaces, can help alleviate and prevent these strains, promoting better posture and reducing the risk of injury.
In some cases, individuals may also experience muscle spasms in the chest or back, which can contribute to the sensation of tightness or pressure in the chest area. These spasms can occur due to overexertion or as a protective response to pain, leading to a cycle of discomfort that can be challenging to break. Understanding the underlying causes of these symptoms is crucial for effective treatment and management, allowing individuals to regain their quality of life and minimize the impact of pain on their daily activities.
Several medical conditions and lifestyle factors can contribute to back pain that results in chest discomfort. Identifying the root cause is crucial for effective management.
Disorders affecting the thoracic spine are among the most common causes of back-related chest pain. These include:
Herniated or Bulging Discs: When the discs between vertebrae in the thoracic spine protrude, they can press on nearby nerves, causing pain that radiates to the chest.
Osteoarthritis: Degeneration of the spinal joints can lead to inflammation and nerve irritation, resulting in discomfort in both the back and chest.
Spinal Stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal can compress nerves and cause pain that extends to the chest area.
Injuries such as muscle strains, ligament sprains, or rib fractures can cause pain that is felt in both the back and chest. Poor posture, especially in people who work long hours at desks, can also lead to chronic muscle tension and discomfort.
Conditions like shingles (herpes zoster) can cause nerve pain in the thoracic region, leading to chest discomfort. Additionally, inflammation of the cartilage connecting ribs to the sternum, known as costochondritis, can cause chest pain that sometimes radiates to the back.
Because chest discomfort can signal serious conditions such as heart attack or pulmonary issues, it is critical to seek prompt medical evaluation if you experience:
Sudden, severe chest pain or pressure
Pain accompanied by shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, or dizziness
Chest pain that radiates to the arm, neck, jaw, or back
Persistent or worsening chest discomfort without a clear cause
If your chest discomfort is mild and associated with back pain, but you are otherwise healthy, it may be appropriate to explore musculoskeletal causes. However, consulting a healthcare professional is always recommended to rule out life-threatening conditions.
Accessing quality medical advice quickly can be essential, especially when dealing with ambiguous symptoms like chest discomfort. Doctronic.ai offers an innovative telehealth platform that combines artificial intelligence with real doctors to provide fast, reliable, and affordable care. With over 10 million users, Doctronic is revolutionizing how patients receive primary care by offering free AI doctor visits and inexpensive video consultations with licensed physicians available 24/7 across all 50 states.
Through Doctronic.ai, patients can get an initial AI-powered assessment that synthesizes the latest peer-reviewed medical research, offering comprehensive answers and treatment recommendations within moments. If needed, patients can then schedule a telehealth video visit with a real doctor for personalized care without leaving home. This approach ensures timely evaluation of symptoms like chest discomfort and back pain, helping users understand whether urgent care is necessary or if conservative treatment is appropriate.
Accurate diagnosis is the first step toward effective treatment. Healthcare providers typically begin with a detailed history and physical examination to distinguish between cardiac and non-cardiac causes of chest pain. Imaging studies such as X-rays or MRI scans may be ordered to evaluate the spine and chest structures.
Treatment depends on the underlying cause, but often includes:
Physical Therapy: Exercises to improve posture, strengthen muscles, and increase flexibility can alleviate musculoskeletal pain.
Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, or muscle relaxants may be recommended.
Heat or Cold Therapy: Applying heat or ice packs can reduce inflammation and soothe sore muscles.
Lifestyle Modifications: Ergonomic adjustments at work, regular exercise, and stress management can prevent recurrence.
In some cases, more advanced interventions such as injections or surgery may be necessary, particularly if nerve compression is severe.
Maintaining a healthy spine and chest wall can reduce the risk of pain and discomfort. Some preventive measures include:
Practicing good posture, especially when sitting for long periods
Engaging in regular physical activity to strengthen the back and core muscles
Using proper techniques when lifting heavy objects
Taking breaks to stretch and move during sedentary activities
Managing stress to reduce muscle tension
Early intervention at the first signs of back pain can prevent progression and reduce the likelihood of chest discomfort developing.
 When Back Pain Radiates to the Chest
When Back Pain Radiates to the ChestChest discomfort can arise from a variety of causes, including pain originating in the back. Understanding the connection between back pain and chest discomfort helps in identifying the source and seeking appropriate care. While serious conditions must always be ruled out, musculoskeletal issues involving the thoracic spine and surrounding muscles are common culprits.
For those experiencing chest discomfort linked to back pain, utilizing advanced telehealth services like Doctronic.ai can provide rapid, reliable assessments and access to medical professionals from the comfort of home. This innovative platform combines AI-driven medical knowledge with personalized care, ensuring patients receive the right guidance promptly.
Remember, if chest discomfort is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms, seek emergency medical care immediately. Otherwise, exploring musculoskeletal causes with the help of telehealth or in-person providers can lead to effective treatment and relief.
If you're dealing with chest discomfort that may be linked to back pain, don't wait in uncertainty. Doctronic offers a revolutionary approach to healthcare, providing fast, accurate, and personalized medical advice through our AI doctor. Get the most modern medical insights in seconds and enjoy the convenience of a virtual visit with our compassionate doctors, available 24/7 across all 50 states. With over 10 million satisfied users, Doctronic is your partner in health, offering free AI doctor visits and affordable telehealth video visits under $40. Skip the line. Talk to an AI Doctor Now, for free.
Thoracic spine problems frequently cause chest discomfort through nerve irritation or muscle strain, distinguishable from heart issues by movement-related worsening and positional relief. The key is recognizing that spinal-origin chest pain typically improves with rest and worsens with physical activity. If you're experiencing unexplained chest discomfort, Doctronic can help evaluate your symptoms and determine appropriate next steps.
Experiencing chest discomfort can be alarming, often prompting thoughts of heart-related issues. However, the source of chest pain is not always cardiac in nature. One common [...]
Read More