Blood Pressure Monitor
Understanding Blood Pressure and Why Monitoring MattersBlood pressure represents the dynamic interplay between your heart's pumping action and the resistance of your [...]
Read More
Medically reviewed by Oghenefejiro Okifo | MD, Harvard Medical School | Henry Ford Hospital - Detroit, MI on August 19th, 2023.
Acute episodes typically resolve within 2-6 weeks with conservative treatment, while chronic cases lasting over 12 weeks affect approximately 20% of people who initially experience acute pain.
Red flag symptoms requiring immediate medical attention include loss of bladder/bowel control, progressive leg weakness, or severe pain following trauma—these may indicate nerve compression or fracture.
Core strengthening exercises performed 2-3 times weekly can reduce recurrence risk by up to 35%, with planks and bird-dog exercises being most effective for spinal stability.
NSAIDs like ibuprofen (400-600mg every 6-8 hours) provide better pain relief than acetaminophen for inflammatory conditions, but shouldn't exceed 10 days without medical supervision.
The "90-degree rule" for lifting—keeping knees bent at 90 degrees while lifting objects close to your body—reduces spinal load by 50% compared to bending at the waist.
Back pain is a common issue that affects many people at some point in their lives. Your spinal column is your body's main structural support, and it needs to be stable enough to keep you upright while also being flexible enough for movement. In this article, we'll explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of back pain to help you better understand and manage this condition.
Back problems can develop over time due to various factors, including:
Poor posture, such as sitting incorrectly at a desk or behind the steering wheel
Repetitive motions or overexertion
Improper lifting techniques
Injuries from contact sports, accidents, or falls
Osteoarthritis, which can cause wear and tear on the cartilage between vertebrae
Pregnancy, which can put additional stress on the spine and legs due to hormonal changes and weight gain
Back pain can manifest in various ways, including:
Dull ache or sharp, shooting pain
Muscle spasms or cramps
Radiating pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the legs or arms
If you experience uncontrolled peeing or pooping, inability to pee, or muscle weakness along with back pain, seek immediate medical attention as these could be signs of a serious problem like spinal cord compression.
If your back pain is severe, persists for more than 6 weeks, or spreads to other areas, it's important to see a doctor. During your exam, your doctor will assess your range of motion and nerve function. They may also recommend imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans to help identify the underlying cause of your pain.
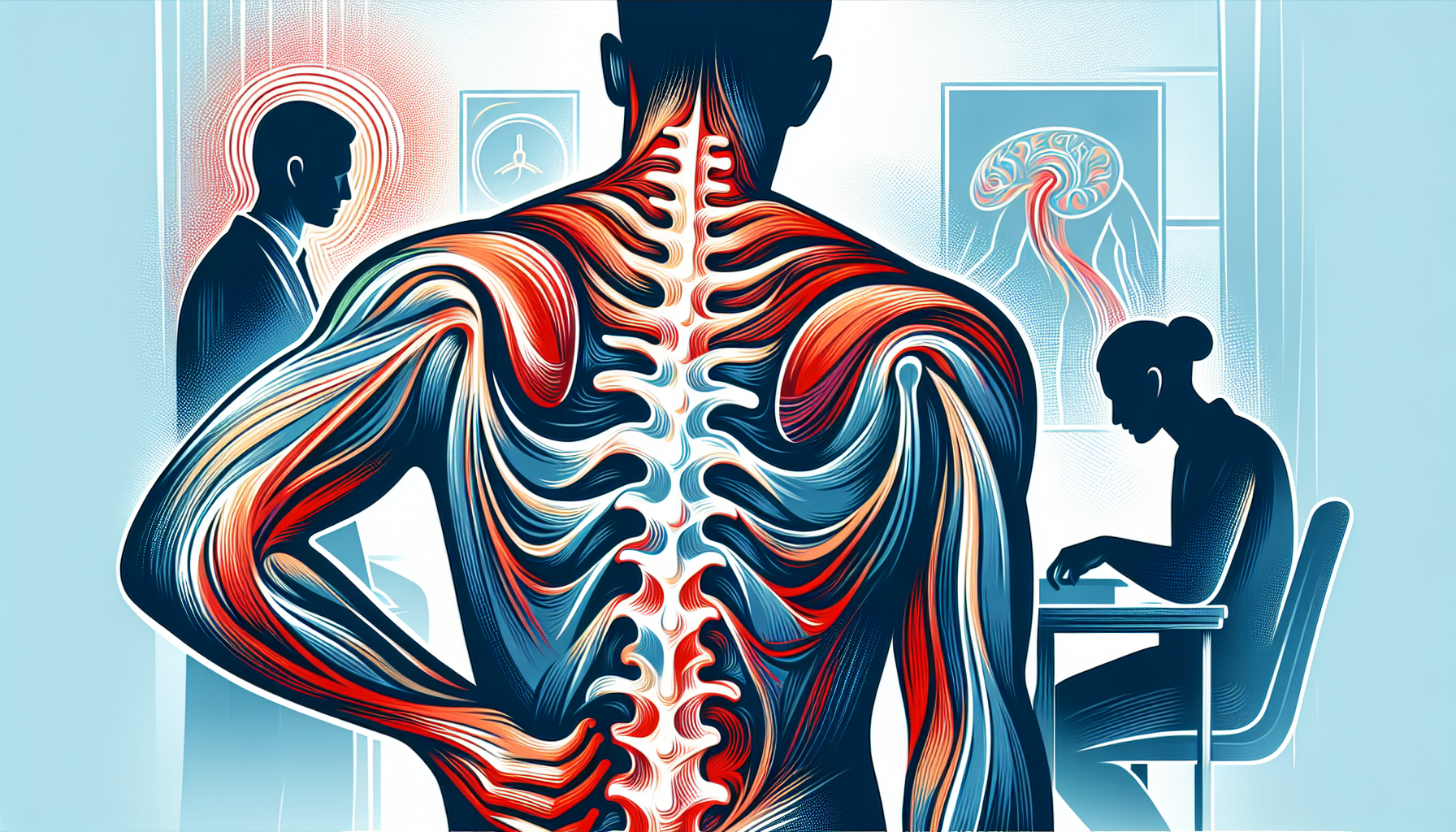
Treatment for back pain depends on the specific cause and location of the pain. In most cases, gentle exercise and physical therapy can help alleviate pain, improve flexibility, and strengthen the muscles that support your spine. Over-the-counter pain relievers, ice, and heat can also provide relief.
For more severe cases, your doctor may prescribe stronger medications, but it's important to use them cautiously to avoid drowsiness or dependence. Complementary therapies such as chiropractic spinal manipulation, acupuncture, and massage can also be beneficial. Surgery may be necessary in cases of damaged bones, herniated disks, or pinched nerves.
To help prevent back pain, consider the following tips:
Exercise regularly to strengthen your core and back muscles
Practice good posture when sitting, standing, and walking
Use proper lifting techniques, engaging your hips and knees while keeping your back straight
Sleep on your side with a medium-firm mattress
Avoid smoking, as it can restrict blood flow and nutrient supply to your muscles and tissues
By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for back pain, as well as implementing preventive measures, you can better manage this common condition and maintain a healthy, pain-free back. If your back pain persists or worsens, don't hesitate to seek medical advice from a qualified healthcare professional.
Most episodes resolve naturally within weeks using a combination of gentle movement, appropriate pain medication, and avoiding bed rest for more than 1-2 days. Focus on maintaining activity levels while avoiding movements that worsen symptoms, as complete rest often delays recovery. If you're experiencing persistent pain, numbness, or concerning symptoms, Doctronic can help you determine when professional evaluation is needed.
Understanding Blood Pressure and Why Monitoring MattersBlood pressure represents the dynamic interplay between your heart's pumping action and the resistance of your [...]
Read MoreHow Calcium Channel Blockers Work in Your BodyTo understand calcium channel blockers, it's essential to grasp calcium's vital role in cardiovascular function. [...]
Read MoreCommon Side Effects by Medication ClassACE inhibitors, one of the most frequently prescribed blood pressure medication categories, are known for causing a persistent dry [...]
Read More