Utah AI Prescription Refill Program
Routine Refills, ReimaginedMissed medications are one of the largest drivers of preventable health outcomes in the country, responsible for over $100 billion in avoidable [...]
Read More
Medically reviewed by Jerome Albert Ecker | MD, Assistant Professor of Medicine, Duke University - Durham, NC on May 20th, 2025.
Allergic reactions typically appear within 2-4 hours of exposure to triggers like nuts, shellfish, or new medications, causing raised, red welts that migrate across the skin.
Viral infections create distinct patterns—chickenpox starts as small red spots that become fluid-filled blisters, while shingles appears as a painful band following nerve pathways on one side of the torso.
Contact dermatitis from irritants like detergents, fragrances, or new fabrics causes localized redness and burning that matches the exact area of skin contact.
Fungal infections like ringworm create circular, scaly patches with raised borders and clearer centers, often spreading outward over 1-3 weeks if untreated.
Seek immediate care if the rash spreads to your face or genitals within 24 hours, develops pus-filled bumps, or occurs with fever above 101°F or difficulty swallowing.
A stomach rash can be uncomfortable and concerning, often prompting questions about its causes and potential treatments.
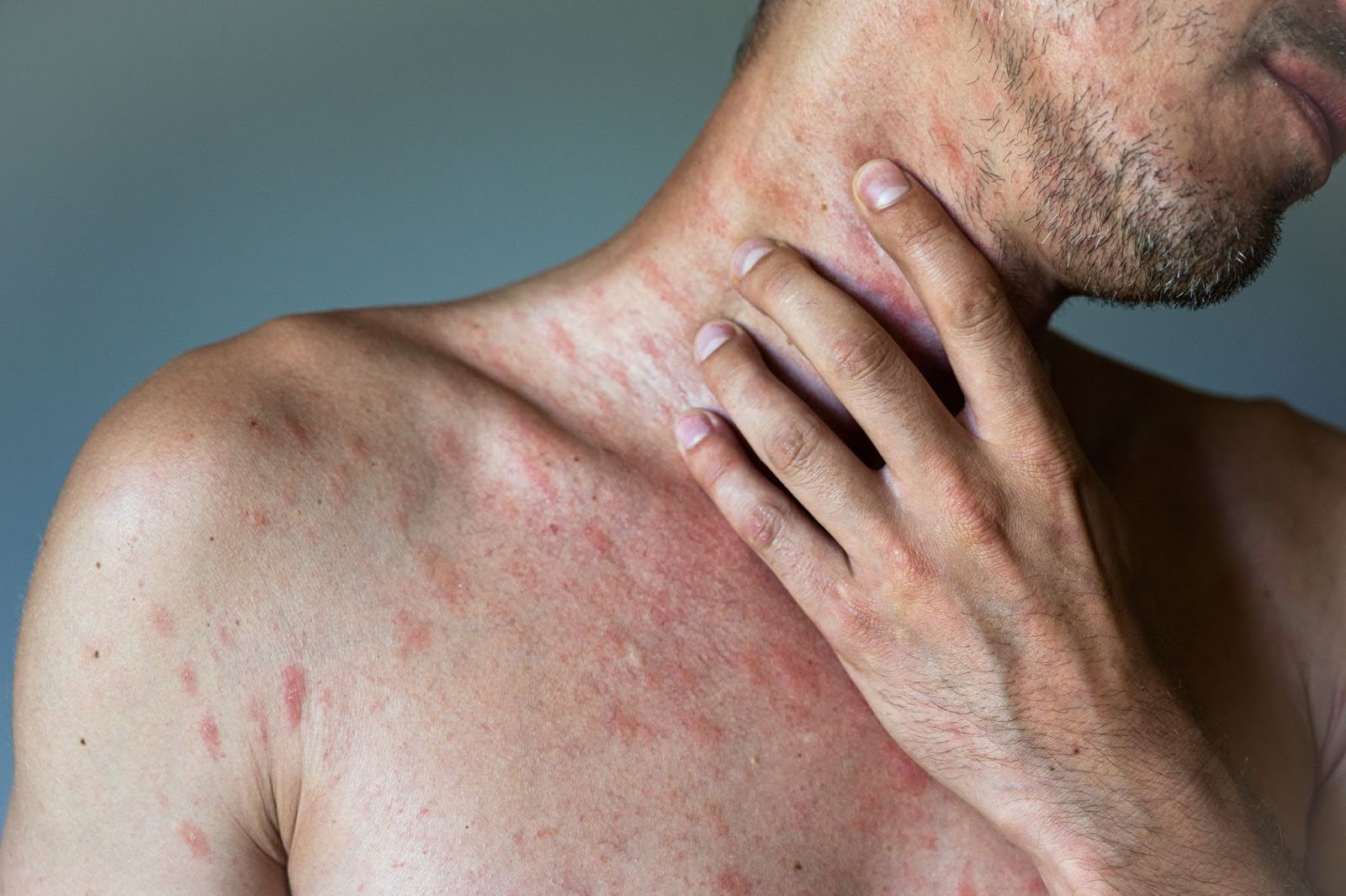 Understanding the underlying factors contributing to a rash is crucial for effective management and relief. This article delves into the various causes of stomach rashes, their symptoms, and possible treatment options.
Understanding the underlying factors contributing to a rash is crucial for effective management and relief. This article delves into the various causes of stomach rashes, their symptoms, and possible treatment options.
Allergic reactions can manifest in numerous ways, including stomach rashes. They may be triggered by food, medications, or environmental factors. Common allergens include nuts, shellfish, certain fruits, and pollen.
When the body encounters an allergen, it releases histamines, leading to inflammation and irritation of the skin. This can result in a rash that may appear red, itchy, and swollen.
Identifying and avoiding the allergen is essential for preventing future outbreaks. In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend skin testing or elimination diets to pinpoint specific allergens and help manage symptoms more effectively.
Several skin conditions can lead to rashes on the stomach. Eczema, psoriasis, and contact dermatitis are among the most common. Each of these conditions has distinct characteristics and triggers:
Eczema: Often characterized by dry, itchy patches, eczema can flare up due to stress, temperature changes, or irritants.
Psoriasis: This chronic condition causes thick, red patches covered with silvery scales, which are often exacerbated by stress, infections, or certain medications.
Contact Dermatitis: This occurs when the skin comes into contact with a substance that causes irritation or an allergic reaction, resulting in a rash.
In addition to these conditions, lifestyle factors such as diet and hygiene can also significantly affect skin health.
For example, a diet high in processed foods may contribute to inflammation, while maintaining proper skin hydration can help alleviate symptoms of eczema. Furthermore, using gentle, fragrance-free soaps and moisturizers can minimize irritation and support the skin's natural barrier.
If you're unsure which habits or products are right for your skin type, Doctronic can help. This AI-powered tool provides personalized skincare guidance, helping you understand what’s affecting your skin and how to improve it without leaving your home.
Viral and bacterial infections can also lead to a rash on the stomach. Conditions such as chickenpox, shingles, and impetigo are notable examples. Each of these infections presents unique symptoms:
Chickenpox: Characterized by itchy blisters that can appear on the stomach and other body parts.
Shingles: A reactivation of the chickenpox virus, shingles can cause a painful rash that often appears as a stripe of blisters.
Impetigo: A bacterial infection that can cause red sores, often around the mouth and nose, but can also spread to the stomach.
Infections can also vary in severity, with some requiring immediate medical attention. For example, while chickenpox is generally mild in children, it can lead to complications in adults or those with weakened immune systems.
Similarly, shingles can cause intense pain and discomfort, often necessitating antiviral medications for effective management.
It's crucial to monitor any rash for signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or pus, and to seek medical advice if these symptoms arise.
Autoimmune disorders occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells. Conditions such as lupus and dermatomyositis can lead to rashes on various parts of the body, including the stomach.
These rashes may be accompanied by other systemic symptoms, such as fatigue and joint pain. In some cases, the skin manifestations can serve as a warning sign, prompting individuals to seek medical attention before more severe symptoms develop.
Diagnosing an autoimmune disorder typically involves a combination of blood tests and physical examinations. Physicians may look for specific autoantibodies or markers indicating an immune response against the body’s tissues.
Treatment often focuses on managing symptoms and suppressing the immune response. This can include corticosteroids, immunosuppressive drugs, and lifestyle modifications to reduce triggers, such as stress and certain dietary factors.
Regular follow-ups are crucial, as autoimmune conditions can fluctuate over time, requiring adjustments in treatment plans.
Heat rash, or prickly heat, occurs when sweat ducts become blocked, leading to small, itchy bumps on the skin. This condition is more common in hot, humid weather and can affect any area of the body, including the stomach.
The rash typically appears as clusters of red or pink bumps, which can be uncomfortable and irritating. Keeping the skin cool and dry is essential for preventing and treating heat rash. Wearing loose-fitting clothing made from breathable fabrics can minimize friction and allow sweat to evaporate more easily.
In addition to environmental factors, certain activities can exacerbate heat rash, such as exercising in high temperatures or spending extended periods in hot baths. For those prone to heat rash, it is advisable to take frequent breaks in a cooler environment and stay hydrated.
Over-the-counter topical treatments, such as calamine lotion or hydrocortisone cream, may provide relief from itching and inflammation. In severe cases, persistent heat rash might require consultation with a dermatologist to explore other underlying skin conditions that could be contributing to the problem.
Fungal infections, such as ringworm or candidiasis, can also cause stomach rashes. These infections thrive in warm, moist environments, leading to red, itchy patches. Despite its name, ringworm is not caused by a worm but rather by a fungal organism that can spread through direct contact or contaminated surfaces.
Symptoms often include a circular, raised rash with a clearer center, which can be particularly alarming for those unfamiliar with the condition. Treatment typically involves antifungal medications, which can be topical or oral, depending on the severity of the infection.
In addition to traditional antifungal treatments, proper hygiene and drying the affected area are critical steps in managing and preventing fungal infections.
Individuals with compromised immune systems or those who frequently experience skin folds, such as in the stomach area, may be at higher risk for recurrent infections.
It’s important to note that while over-the-counter antifungal creams can be effective for mild cases, persistent or worsening symptoms should prompt a visit to a healthcare provider for a more comprehensive evaluation and tailored treatment plan.
While rashes are the primary symptom, they often come with additional signs that can help in diagnosing the underlying cause. Common symptoms that may accompany a stomach rash include:
Itching: This is a common symptom associated with most rashes.
Redness: Inflammation often leads to a red appearance in the affected area.
Swelling: Some rashes may cause localized swelling or puffiness.
Blisters: Certain infections or allergic reactions may result in blister formation.
Pain or Discomfort: Some rashes may be painful, especially if they are caused by infections or autoimmune disorders.
In addition to these symptoms, gastrointestinal disturbances may also arise, particularly if the rash is linked to an allergic reaction or infection. Patients might experience nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea, which can further complicate the clinical picture.
These digestive symptoms can indicate a systemic response to allergens or pathogens, suggesting that the rash might not be an isolated issue but rather part of a broader condition affecting the body. Keeping track of these accompanying symptoms can be crucial for healthcare providers in determining the right course of treatment.
Moreover, the duration and progression of the rash and its associated symptoms can provide vital clues. For example, a rash that appears suddenly and is accompanied by fever may suggest an infectious etiology. In contrast, a chronic rash that persists over weeks or months might point towards a dermatological condition like eczema or psoriasis.
Observing any changes in the rash, such as spreading or changes in color or texture, can also be critical in guiding diagnosis and management. Understanding these nuances can empower individuals to seek timely medical advice and ensure that they receive appropriate care for their symptoms.
 While many rashes can be managed at home, certain situations warrant professional medical evaluation. It is advisable to seek medical attention if:
While many rashes can be managed at home, certain situations warrant professional medical evaluation. It is advisable to seek medical attention if:
The rash is widespread or rapidly spreading.
It is accompanied by fever or other systemic symptoms.
The rash does not improve with over-the-counter treatments.
There are signs of infection, such as pus or increased redness.
The individual experiences difficulty breathing or swelling of the face or throat, which could indicate an allergic reaction.
In addition to these warning signs, it is crucial to consider the duration of the rash. If a rash persists for more than a few days without any signs of improvement, it may indicate an underlying condition requiring further investigation.
Conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, or even autoimmune disorders can manifest as rashes and may necessitate a tailored treatment approach. Therefore, monitoring the rash's progression and any accompanying symptoms is essential for timely intervention.
Furthermore, individuals with compromised immune systems or pre-existing skin conditions should be particularly vigilant. For these individuals, even minor rashes can escalate quickly and lead to more severe complications.
Consulting a healthcare provider early on can help prevent potential complications and ensure that appropriate treatments are initiated. Remember, when in doubt, avoiding caution and seeking professional advice to safeguard your health is always better.
Diagnosing the cause of a stomach rash typically involves a thorough medical history and physical examination. Healthcare providers may ask about:
Recent exposures to allergens or irritants
Family history of skin conditions or allergies
Other symptoms that may accompany the rash
In some cases, further testing may be necessary. This can include:
Skin Biopsy: A small sample of skin may be taken for laboratory analysis to determine the cause of the rash.
Allergy Testing: This can help identify specific allergens that may be triggering the rash.
Blood Tests: These may be used to check for underlying conditions, such as autoimmune disorders.
In addition to these diagnostic methods, healthcare providers may also consider the patient's lifestyle and environmental factors that could contribute to the rash. For example, dietary habits, exposure to pets, or even stress levels can play a significant role in skin health.
Patients might be asked to keep a diary of their daily activities, food intake, and any new products they have used on their skin to help pinpoint potential triggers. This holistic approach not only aids in identifying the rash's cause but also empowers patients to take an active role in their treatment.
Moreover, the appearance of the rash itself can provide valuable clues for diagnosis. Rashes can vary widely in color, texture, and distribution, and these characteristics can indicate different underlying issues.
For example, a red, itchy rash may suggest an allergic reaction, while a scaly, dry patch could point to a condition like eczema or psoriasis. By carefully examining these details, healthcare providers can narrow the list of possible diagnoses and tailor their approach to each patient, ensuring a more effective treatment plan.
Treatment for a stomach rash varies depending on the underlying cause. Here are some common approaches:
For many rashes, topical treatments can provide relief. These may include:
Corticosteroid Creams: These reduce inflammation and itching.
Antihistamines: Oral or topical antihistamines can help alleviate itching associated with allergic reactions.
Moisturizers: For conditions like eczema, keeping the skin hydrated is essential.
Antifungal Creams: Topical antifungals, like clotrimazole or terbinafine, can be used to relieve and eliminate symptoms.
In more severe cases, oral medications may be necessary. These can include:
Antibiotics: For bacterial infections like impetigo.
Antifungal Medications: For fungal infections affecting the stomach area.
Immunosuppressants: In cases of autoimmune disorders, these medications may be prescribed to reduce the immune response.
In addition to medical treatments, certain lifestyle changes and home remedies can help manage rashes. These include:
Avoiding Irritants: Identifying and avoiding products that irritate the skin can help prevent flare-ups.
Wearing Loose Clothing: This can help reduce friction and irritation on the skin.
Using Cool Compresses: Applying a cool, damp cloth to the rash can relieve itching and discomfort.
While not all rashes can be prevented, there are measures that can reduce the risk of developing a rash on the stomach:
Maintain Good Hygiene: Regular bathing and keeping the skin clean can help prevent infections.
Moisturize Regularly: Keeping the skin hydrated can help prevent conditions like eczema.
Avoid Known Allergens: If allergies are known, avoiding contact with allergens is key.
Wear Breathable Fabrics: Cotton and other breathable materials can help reduce irritation and sweating.
A stomach rash can arise from various causes, ranging from allergic reactions to infections and skin conditions. Understanding the underlying factors is essential for effective treatment and prevention.
While many rashes can be managed at home, it is crucial to seek medical attention if symptoms worsen or do not improve. By taking proactive measures and being aware of potential triggers, individuals can better manage their skin health and minimize the occurrence of stomach rashes.
Not sure what’s causing your rash? Get quick, expert-backed insights from the comfort of your home with Doctronic, your trusted AI health companion.
Most stomach rashes resolve with proper identification and treatment of the underlying cause, whether allergic, infectious, or irritant-related. Quick medical evaluation prevents complications and ensures appropriate treatment rather than guessing with over-the-counter remedies. If you're experiencing persistent or concerning symptoms, Doctronic can help you determine the likely cause and next steps.
Routine Refills, ReimaginedMissed medications are one of the largest drivers of preventable health outcomes in the country, responsible for over $100 billion in avoidable [...]
Read MoreWhy Tailbone Pain HappensThat sharp ache when you sit down. The lingering discomfort makes driving unbearable. Tailbone pain disrupts daily life in ways most people never [...]
Read MoreWhen most people think of preeclampsia, they immediately associate it with dangerously high blood pressure during pregnancy. However, a lesser-known but equally serious [...]
Read More