Swollen ankles are a common complaint that ranges from benign and temporary to signs of a serious medical problem. Understanding the likely causes, when to be concerned, and what to do next can help prevent complications and get you back on your feet. This article outlines common and less common reasons for ankle swelling, how clinicians evaluate it, immediate steps to take at home, and when telehealth or in-person care is needed.
What Does "Swollen Ankles" Really Mean?
Swelling in the ankles usually reflects the accumulation of extra fluid in the tissues, a condition known medically as peripheral edema. Often, the swelling is evident in the lower legs and may be more pronounced at the end of the day or after long periods of standing. It can be one-sided or affect both ankles symmetrically, and the appearance and associated symptoms help guide the cause.
Some people notice pitting, when pressing a finger into the swollen area leaves an indentation that slowly fills back in, while others report tightness, difficulty fitting shoes, or redness and warmth. Each of these clues narrows down the likely causes.
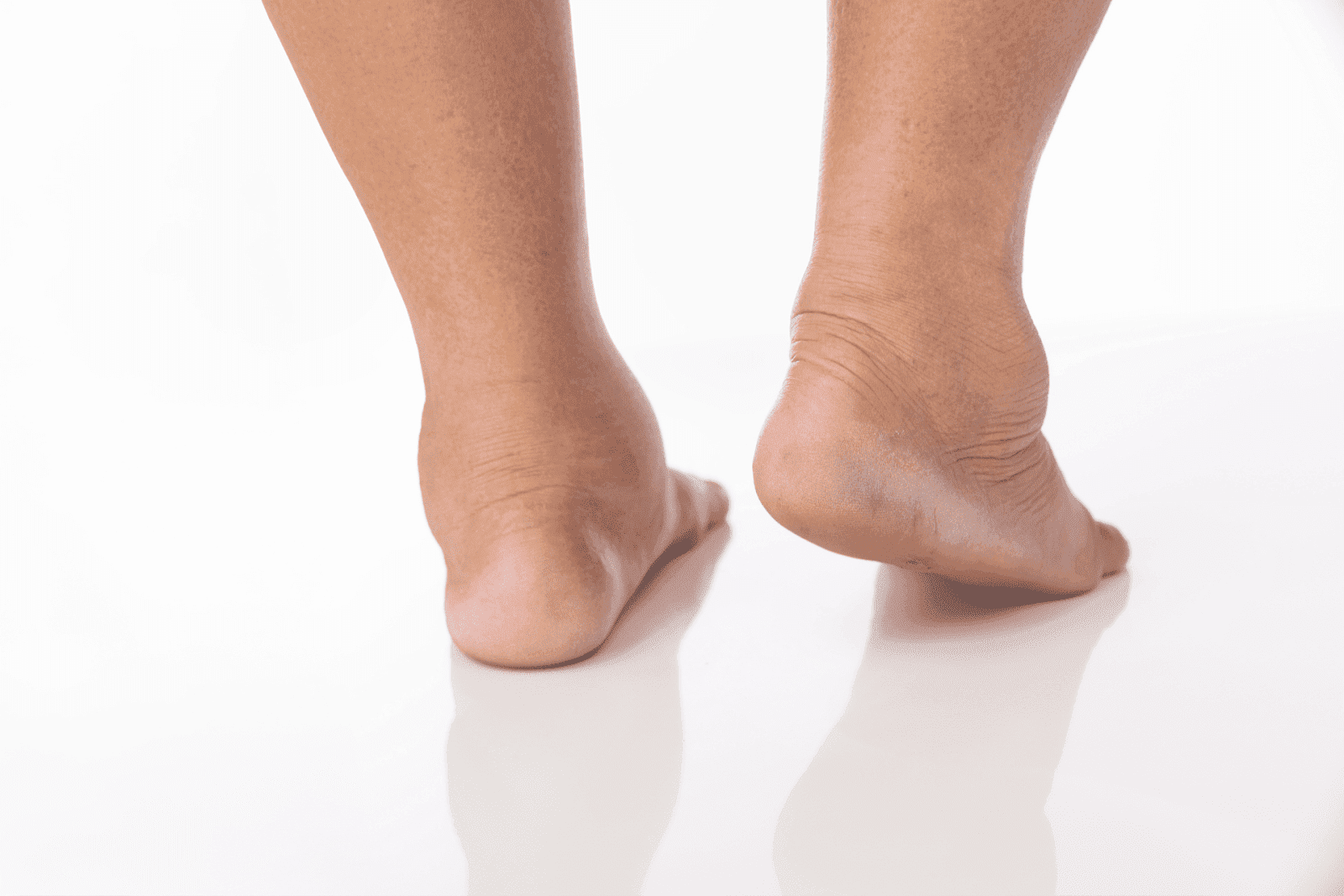 Common, Non-Emergency Causes
Common, Non-Emergency Causes
Many causes of swollen ankles are benign or manageable with lifestyle changes. These should be considered first, especially in otherwise healthy adults.
Gravity and Immobility
Sitting or standing for long periods causes blood and fluid to pool in the legs. Travelers, people who work on their feet, or those with sedentary jobs often notice ankle swelling in the evening that improves with elevation or movement.
Salt, Diet, and Dehydration
High dietary sodium can cause the body to retain fluid. Paradoxically, dehydration can also promote fluid retention when the body conserves water. Reducing salt intake and ensuring adequate hydration often reduces mild, recurrent ankle swelling.
Medications
Several commonly prescribed drugs can cause ankle swelling as a side effect. Notable examples include calcium channel blockers (used for high blood pressure), certain diabetes medications, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and corticosteroids. If ankle swelling begins after starting a new medication, the prescriber should be notified.
Injury and Overuse
An acute sprain, fracture, or overuse injury can lead to localized swelling, often accompanied by pain, bruising, and difficulty bearing weight. Swelling due to mechanical injury typically affects one side and is linked to a specific event.
Medical Conditions That Cause Ankle Swelling
When swelling is persistent, progressive, or accompanied by other symptoms, underlying medical conditions should be considered. These range from venous problems to systemic disease.
Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI)
CVI occurs when the valves in the leg veins are damaged or weakened, allowing blood to pool. This condition causes bilateral swelling that worsens throughout the day, often with aching, heaviness, skin discoloration, and varicose veins. Compression stockings, exercise, and weight management can help; advanced cases may require vascular interventions.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
A blood clot in a deep leg vein can cause sudden, painful swelling of one leg or ankle. DVT is a medical emergency because clots can travel to the lungs and cause a pulmonary embolism. Red flags include rapid onset swelling, significant pain, warmth, and redness in one leg.
Heart Failure
When the heart cannot pump effectively, fluid can back up into the peripheral tissues, producing bilateral ankle swelling that usually increases as the day progresses. Heart failure-related edema is often accompanied by shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling in other areas, like the abdomen.
Kidney Disease
The kidneys regulate fluid and electrolyte balance. When kidney function declines, the body can retain fluid, leading to swelling in the legs and ankles. Associated symptoms may include changes in urine output, foamy urine, and generalized tiredness.
Liver Disease
Advanced liver disease can reduce the production of albumin, a protein that helps keep fluid inside blood vessels. Low albumin levels lead to fluid leaking into tissues and causing swelling, usually accompanied by abdominal swelling (ascites), jaundice, and other systemic signs.
Lymphedema
Lymphedema results from impaired lymphatic drainage and typically causes non-pitting swelling that may be accompanied by skin changes, thickening, and recurrent infections. It often develops after surgery, radiation, infection, or in congenital conditions affecting lymphatic vessels.
Infection (Cellulitis)
Skin and soft tissue infections, such as cellulitis, cause localized swelling, redness, warmth, and tenderness. These infections usually require prompt antibiotic treatment and sometimes further care if the infection is severe or spreading.
When Swollen Ankles Are an Emergency
Most ankle swelling is not immediately life-threatening, but certain signs warrant urgent evaluation. Rapid identification of emergencies like DVT and severe infections can save lives.
Red Flags to Seek Immediate Care
Seek urgent medical attention if any of the following occur: sudden severe swelling in one leg, intense pain, warmth and redness of the limb, shortness of breath, chest pain, fainting, or confusion. These symptoms may indicate a blood clot, pulmonary embolism, or other serious conditions.
For non-urgent but concerning symptoms, such as persistent swelling despite home measures, progressive shortness of breath, or new swelling after starting medications, prompt evaluation by a clinician is recommended.
Diagnosis: What Clinicians Look For
Evaluation typically begins with a careful history and physical exam, focusing on onset, progression, distribution (one or both legs), associated symptoms, medical history, and medications. This guides further testing.
Key Questions and Physical Findings
Clinicians ask about recent travel, immobility, surgeries, injuries, heart or kidney disease, liver disease, and medication changes. They check for pitting, skin changes, varicose veins, temperature differences, and pulses. A positive Homan’s sign (calf pain on dorsiflexion) has limited accuracy and is not relied upon.
Tests Commonly Ordered
Depending on findings, tests may include blood work (CBC, kidney and liver function, albumin, BNP for heart failure), D-dimer testing, Doppler ultrasound for suspected DVT, EKG, and chest imaging if cardiopulmonary symptoms are present, and sometimes lymphoscintigraphy for suspected lymphedema. Imaging and lab tests are tailored to the most likely causes based on the initial assessment.
At-Home Care and Self-Help Strategies
For mild swelling without red flags, several simple measures help reduce fluid buildup and improve symptoms. These are safe starting points and often effective.
Elevation and Movement
Elevate the legs above heart level for 30 minutes several times a day. Walking and calf muscle exercises promote venous return and reduce pooling. Avoid prolonged periods of standing or sitting; stand and move every 30–60 minutes if possible.
Compression Stockings
Graduated compression stockings reduce venous pooling and are especially helpful for people with chronic venous insufficiency or jobs that require prolonged standing. Proper fit is important; professional fitting may be recommended for severe cases.
Diet and Fluid Management
Reducing salt intake, maintaining a healthy weight, and staying well-hydrated often improve mild swelling. Alcohol and excessive carbohydrate consumption can also exacerbate fluid retention in some individuals.
Pain and Inflammation Control
Mild pain from overuse or injury may respond to rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). If over-the-counter pain relievers are considered, be mindful that NSAIDs can sometimes worsen fluid retention in sensitive individuals.
When to Use Telehealth vs in-Person Care
Telehealth is an excellent first step for many people with swollen ankles, especially when the symptoms are mild to moderate and there are no red flags. Virtual visits allow rapid triage, medication review, and recommendations for home care or urgent evaluation if needed.
For urgent concerns, sudden one-sided swelling, severe pain, signs of infection, or cardiopulmonary symptoms, direct in-person evaluation or emergency care is necessary.
How Doctronic.ai Can Help
Digital health platforms make accessing medical advice easier and faster. Doctronic.ai provides free AI-driven doctor visits on its website, delivering rapid, research-backed guidance for symptoms like ankle swelling. The service synthesizes peer-reviewed medical knowledge to offer diagnostic suggestions, treatment options, and next-step recommendations.
For those seeking a live telehealth visit, Doctronic also offers affordable video visits with licensed doctors, available 24/7 in all 50 states for under $40. This combination of AI triage and inexpensive clinician consultations makes it simple to get timely advice and determine whether urgent in-person care is needed. Visit Doctronic.ai to start an AI visit or schedule a doctor video visit.
Prevention and Long-Term Management
Preventing recurrent ankle swelling often focuses on managing the underlying cause and adopting healthy habits that support vascular and renal function.
Lifestyle Measures
Maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly (especially walking and calf-strengthening activities), avoiding prolonged immobility, and wearing proper footwear all reduce the risk of recurrent swelling. Dietary interventions, moderating salt intake and staying hydrated, are foundational.
Medical Follow-Up
If ankle swelling is persistent or linked to chronic conditions like heart failure, kidney disease, or venous insufficiency, ongoing care with appropriate specialists is essential. Treatment may include diuretics for fluid management, procedures to treat venous reflux, or therapies targeting the underlying disease. Doctronic.ai can be used for follow-up questions, medication adjustments, and monitoring, while coordinating referrals as needed.
Special Populations: Pregnancy, Older Adults, and Athletes
Certain groups have unique considerations when it comes to ankle swelling. Recognizing these differences helps tailor management safely and effectively.
Pregnancy
Mild swelling in pregnancy is common and often due to increased blood volume, hormonal changes, and pressure from the growing uterus on pelvic veins. However, sudden or severe swelling, particularly if accompanied by high blood pressure or protein in the urine, requires immediate evaluation for preeclampsia.
Older Adults
Aging increases the likelihood of venous insufficiency, medication side effects, heart and kidney disease, and mobility-related pooling. Careful review of medications and regular monitoring for systemic causes are important in older patients.
Athletes
In athletes, ankle swelling is often due to sprains, overuse injuries, or compartment syndromes. Appropriate rest, graded return to activity, and physical therapy reduce long-term risk. Any suspicion of a stress fracture or severe ligament injury merits imaging and specialist input.
Putting It Together: Practical Next Steps
When faced with swollen ankles, a practical approach prevents unnecessary worry while ensuring dangerous conditions are not missed.
Quick Checklist
Assess for red flags: sudden one-sided swelling, severe pain, shortness of breath, chest pain, fever, or spreading redness; these require immediate care.
Try conservative measures: elevation, movement, compression stockings, salt reduction, and a brief trial of home care if no red flags.
Review medications: check if a recent change could explain the swelling and consult the prescriber.
Use telehealth for triage: digital services can provide rapid guidance and determine if in-person care or testing is needed. Platforms that combine AI triage with affordable clinician visits offer a convenient first step.
Next Steps if Swelling Persists
If swelling does not improve with home measures within a few days, worsens, or is associated with systemic symptoms, arrange clinical evaluation. Diagnostic testing can then be tailored to the most likely causes identified in the history and exam.
 How an AI-Enabled Telehealth Service Speeds Care
How an AI-Enabled Telehealth Service Speeds Care
AI-driven triage tools and virtual visits reduce delays in care by offering immediate, evidence-informed assessments that point patients toward the right level of care. Rather than waiting for an in-person appointment, most patients can get a next-step plan within minutes, advice that may include home care, prescription adjustments, or urgent referral.
Doctronic is one example of a company making this model accessible. Headquartered in New York City and servicing millions of users, Doctronic offers free AI doctor visits on its website and affordable telehealth video visits 24/7 in all 50 states. Its AI draws on peer-reviewed medical research to provide high-quality, personalized recommendations and remembers prior visits to provide continuity of care as symptoms evolve. Visit Doctronic.ai to explore options for a rapid assessment and next steps.
Smart Support for Ankle Health
Most swollen ankles are manageable and related to benign causes like gravity, diet, or minor injury. However, a structured approach to evaluation helps identify when swelling signals a more serious problem, such as DVT, heart failure, or infection. Small lifestyle changes and supportive measures often bring relief, and telehealth can provide fast, reliable triage and follow-up. When in doubt, consult a clinician promptly; early assessment is the safest route to recovery and peace of mind.
Remember: sudden, severe, or asymmetric swelling with pain or breathing difficulties requires immediate medical attention. For convenience, consider using modern telehealth resources that offer evidence-based initial assessments and affordable video visits for quick access to medical advice and follow-up care.
Quick Help for Swollen Ankles: Start with an AI Doctor
If you’re worried about ankle swelling or just want rapid, evidence-based guidance, try Doctronic, the #1 AI Doctor. Our AI synthesizes the latest peer‑reviewed medical knowledge, remembers your history, and gives personalized recommendations in seconds. Start with a free AI doctor visit on our website, or book an affordable video visit with a licensed doctor 24/7 in all 50 states for under $40. Over 10 million people have used Doctronic to get faster, smarter, more personal care. Skip the line. Talk to an AI Doctor Now, for free.



 Common, Non-Emergency Causes
Common, Non-Emergency Causes How an AI-Enabled Telehealth Service Speeds Care
How an AI-Enabled Telehealth Service Speeds Care