Utah AI Prescription Refill Program
Routine Refills, ReimaginedMissed medications are one of the largest drivers of preventable health outcomes in the country, responsible for over $100 billion in avoidable [...]
Read More
Medically reviewed by Oghenefejiro Okifo | MD, Harvard Medical School | Henry Ford Hospital - Detroit, MI on December 10th, 2025.
Paragard and Mirena are two popular intrauterine devices (IUDs) offering long-term contraception with distinct features.
Paragard is hormone-free and copper-based, while Mirena releases a low dose of progestin hormone.
Both IUDs provide effective birth control but differ in side effects, duration, and suitability for individual needs.
Understanding these differences helps in choosing the right IUD, with telehealth services like Doctronic.ai offering convenient access to expert advice and prescriptions.
Intrauterine devices, or IUDs, are small, T-shaped devices inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. They are among the most effective reversible birth control methods available today. Paragard and Mirena are two of the most commonly used IUDs, but they work quite differently.
Paragard is a hormone-free IUD that uses copper to prevent pregnancy. The copper acts as a natural spermicide, disrupting sperm movement and preventing fertilization. It can remain effective for up to 10 years, making it a long-lasting option for those seeking hormone-free contraception. Paragard does not affect a woman's menstrual cycle in the same way hormonal methods do; some users may experience heavier periods or increased cramping, especially in the first few months after insertion. However, many appreciate the absence of hormones, which can lead to side effects such as mood changes or weight gain.
Mirena releases a low dose of the hormone levonorgestrel directly into the uterus. This hormone thickens cervical mucus to block sperm and thins the uterine lining to prevent implantation. Mirena is approved for use up to 7 years, providing long-term contraception with additional benefits like reducing heavy menstrual bleeding for some users. Many women find that their periods become lighter or even stop altogether after several months of use, which can be a significant advantage for those who suffer from heavy menstrual cycles. Mirena can also be used to treat conditions like endometriosis, making it a versatile option for many women seeking both contraception and relief from painful symptoms.
Both Paragard and Mirena offer highly reliable contraception, but their effectiveness and lifespan differ slightly.
Both IUDs have a failure rate of less than 1%, making them among the most dependable birth control methods available. Paragard’s effectiveness lasts up to 10 years, while Mirena remains effective for up to 7 years. The choice between them often depends on how long you want protection and whether you prefer hormone-free birth control.
Paragard’s copper design allows it to be used for a decade without replacement. Mirena requires replacement every 5 to 7 years, depending on the specific product version. Both devices can be removed at any time if pregnancy is desired or side effects occur.
Understanding potential side effects is crucial when choosing between Paragard and Mirena. Each IUD has a unique profile that may affect your comfort and health.
Menstrual Changes: Paragard users often experience heavier, longer, or more painful periods, especially in the first few months after insertion.
Copper Allergy: Rarely, some individuals may react to the copper, causing irritation or discomfort.
Cramping: Mild to moderate cramping during and after insertion is common but usually subsides.
Hormonal Effects: Since Mirena releases progestin, some users may experience mood changes, acne, or breast tenderness.
Menstrual Changes: Many users report lighter periods or even amenorrhea (absence of periods) after several months of use.
Spotting: Irregular spotting or bleeding can occur, especially in the first 3 to 6 months.
People with certain health conditions should consult a healthcare provider before choosing an IUD. For example, Paragard may not be suitable for those with Wilson’s disease or copper allergies. Mirena might not be recommended for individuals with hormone-sensitive cancers or unexplained vaginal bleeding. Telehealth platforms like Doctronic.ai offer quick access to medical professionals who can help determine the best option based on your health history.
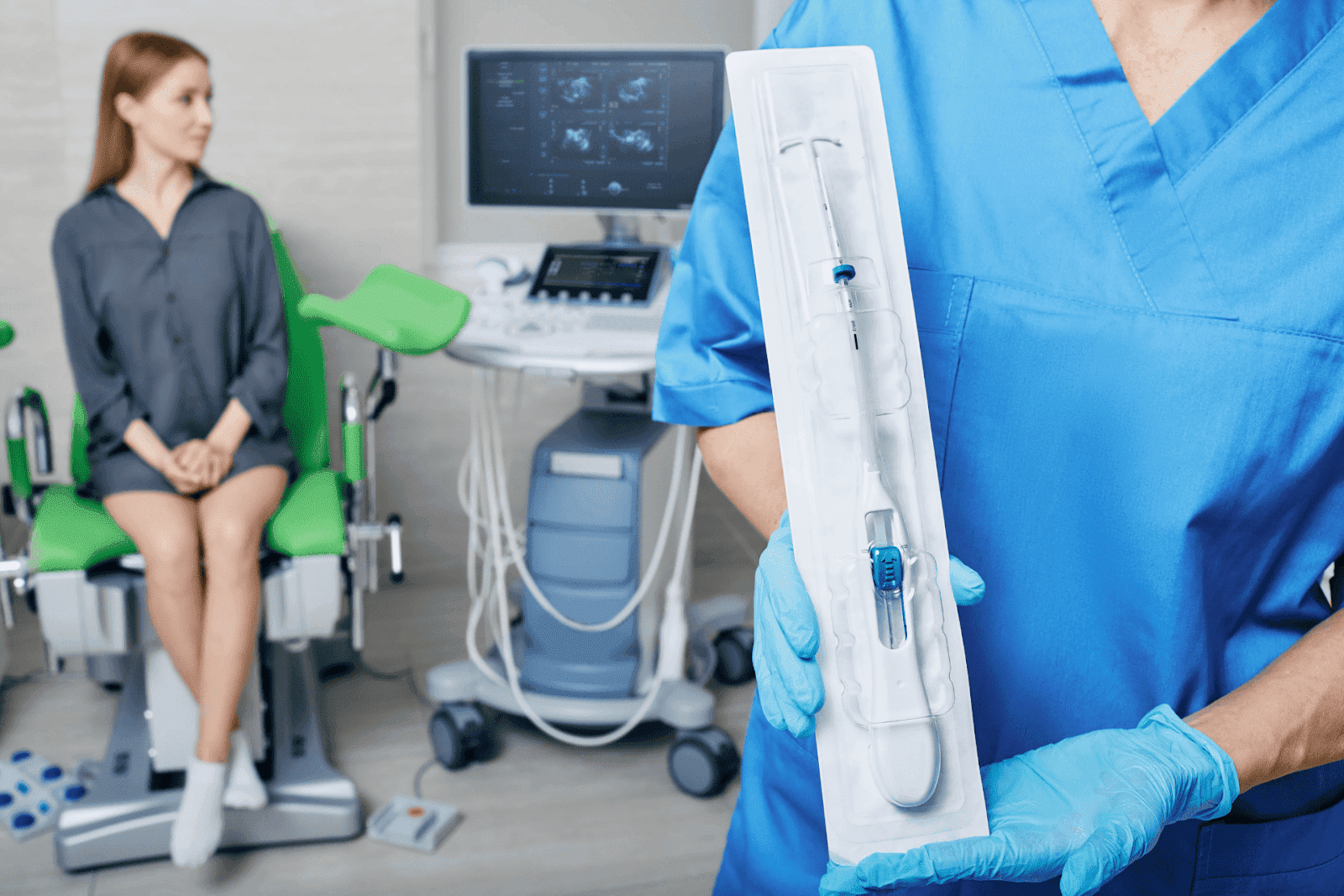 Insertion and Removal Process
Insertion and Removal ProcessBoth Paragard and Mirena require professional insertion and removal by a healthcare provider. The procedure is usually quick but can cause some discomfort.
The healthcare provider will perform a pelvic exam, then insert the IUD through the cervix into the uterus using a thin tube. Some people feel cramping or pressure during this process. It typically takes only a few minutes.
After insertion, mild cramping or spotting is normal for a few days. It’s important to check the IUD strings regularly to ensure the device remains in place. Follow-up visits may be recommended to confirm proper positioning.
Removal is also done by a healthcare professional. The provider gently pulls on the IUD strings to remove the device. If you want to switch IUDs or stop using one, removal can be done at any time.
Deciding which IUD fits your lifestyle and health needs involves weighing several factors.
If you prefer to avoid hormones, Paragard is the clear choice. It offers effective contraception without hormonal side effects. On the other hand, Mirena’s hormones can help reduce heavy periods and may benefit those with menstrual-related symptoms.
Paragard may increase menstrual bleeding and cramping, which might be a drawback for some. Mirena often lightens periods or stops them altogether, which many users find convenient.
Paragard lasts longer, up to 10 years, so it may be better if you want a “set it and forget it” option. Mirena requires replacement sooner, but offers additional benefits beyond contraception.
Getting an IUD usually involves in-person visits, but telehealth can simplify the process by providing expert consultations and prescriptions remotely. Doctronic.ai offers affordable, convenient video visits with licensed doctors available 24/7 across all 50 states. This makes it easier to discuss your options, get personalized recommendations, and arrange for insertion with a local provider.
Choosing between Paragard and Mirena comes down to your personal preferences, health considerations, and lifestyle. Both IUDs offer reliable, long-term contraception but differ in hormone content, side effects, and duration. Consulting with a healthcare provider is essential to finding the best fit for you.
Telehealth platforms like Doctronic.ai make this process easier by connecting you with medical experts who can answer your questions, provide personalized recommendations, and help you access IUD services without the hassle of traditional appointments. With over 10 million users, Doctronic is trusted for fast, smart, and personal care powered by AI.
Mirena is effective immediately if inserted within seven days of the start of your period; otherwise, use backup contraception for seven days. Paragard is effective immediately, regardless of timing.
Pregnancy is rare with both Paragard and Mirena, with failure rates below 1%. If pregnancy occurs, it is important to see a healthcare provider promptly.
Yes, both Paragard and Mirena are approved for people who have never been pregnant. Your healthcare provider can help determine suitability.
Side effects often improve after a few months. If they persist or are severe, consult a healthcare professional. Telehealth services like Doctronic.ai can provide quick advice and support.
Both Paragard and Mirena are considered safe for use during breastfeeding, but it’s best to discuss timing and options with your healthcare provider.
Routine Refills, ReimaginedMissed medications are one of the largest drivers of preventable health outcomes in the country, responsible for over $100 billion in avoidable [...]
Read MoreWhy Tailbone Pain HappensThat sharp ache when you sit down. The lingering discomfort makes driving unbearable. Tailbone pain disrupts daily life in ways most people never [...]
Read MoreWhen most people think of preeclampsia, they immediately associate it with dangerously high blood pressure during pregnancy. However, a lesser-known but equally serious [...]
Read More