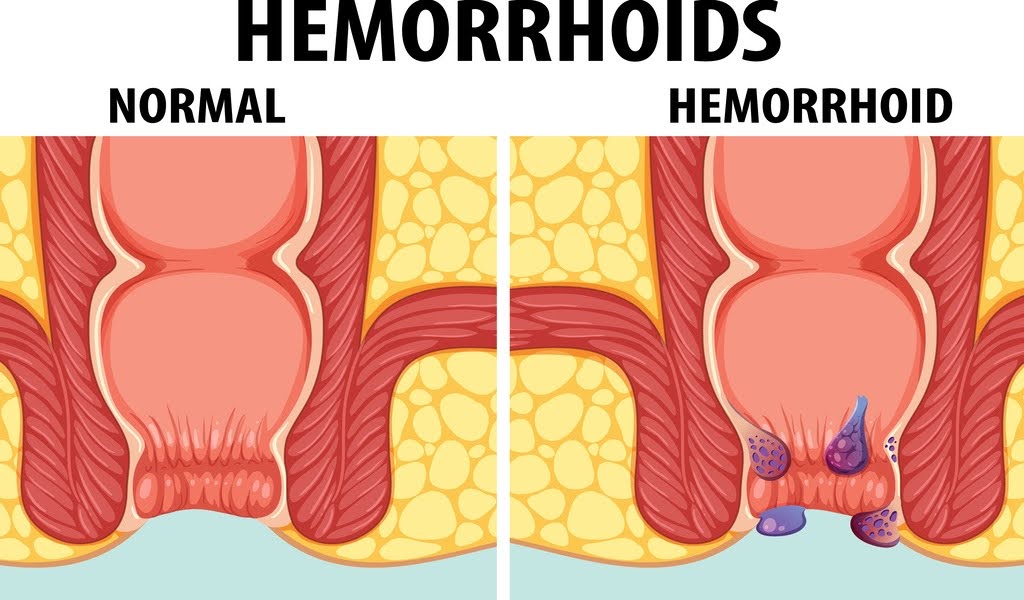
 The human body is a complex system, and understanding its various functions is essential for maintaining overall health. One area that often goes overlooked is the anal region, specifically the differences between a normal anus and the presence of hemorrhoids. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of both conditions, their symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
The human body is a complex system, and understanding its various functions is essential for maintaining overall health. One area that often goes overlooked is the anal region, specifically the differences between a normal anus and the presence of hemorrhoids. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of both conditions, their symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
Understanding the Normal Anus
The anus is the opening at the end of the digestive tract, through which stool exits the body. It is surrounded by muscles known as the anal sphincters, which help control bowel movements. A normal anus functions effectively to allow for the passage of waste without discomfort.
Anatomy of the Anus
The anatomy of the anus is crucial for its function. It consists of several components:
Anal Canal: The short tube that connects the rectum to the outside of the body.
Anal Sphincters: Two muscles that encircle the anal canal, controlling the release of stool.
Rectal Mucosa: The lining of the rectum that helps in the smooth passage of stool.
These components work together to ensure that bowel movements occur smoothly and without pain.
Additionally, the anus is richly supplied with nerve endings, making it highly sensitive to pressure and stretch. This sensitivity plays a critical role in signaling the need to defecate. This sensitivity is essential for the body’s ability to respond appropriately to the presence of stool in the rectum, thus preventing involuntary leakage and maintaining continence.
Normal Functioning
In a healthy individual, the anus allows for the controlled expulsion of feces. The anal sphincters relax during a bowel movement, permitting stool to exit while maintaining a barrier against unwanted leakage at other times. This balance is vital for comfort and hygiene.
Furthermore, the coordination between the anal sphincters and the pelvic floor muscles is crucial; these muscles work in tandem to ensure that defecation is effective and discreet. Any disruption in this coordination can lead to issues such as constipation or fecal incontinence, highlighting the importance of maintaining good digestive health.
Moreover, the anus plays a role in the overall health of the gastrointestinal system. Regular bowel movements are essential for eliminating toxins and waste products from the body. A well-functioning anus contributes to a healthy gut microbiome, as the timely expulsion of stool prevents the buildup of harmful bacteria.
Therefore, understanding the normal function of the anus not only aids in recognizing potential health issues but also emphasizes the importance of dietary choices and hydration in promoting optimal digestive health.
What Are Hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the lower rectum and anus, similar to varicose veins. Depending on their location and severity, they can cause discomfort, pain, and other symptoms. There are two main types: internal and external.
Types of Hemorrhoids
Understanding the types of hemorrhoids is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment:
Internal Hemorrhoids: Located inside the rectum, these hemorrhoids are usually painless but can cause bleeding during bowel movements.
External Hemorrhoids: Found under the skin around the anus, these can be painful and may cause discomfort, especially during bowel movements.
Both types can lead to complications if left untreated, making awareness of their symptoms crucial. In some cases, internal hemorrhoids can protrude outside the anus, a condition known as prolapsed hemorrhoids, which may require medical intervention for relief. Understanding the nuances of these classifications can help individuals seek appropriate care and avoid unnecessary discomfort.
Symptoms of Hemorrhoids
Recognizing the symptoms of hemorrhoids can facilitate early intervention. Common symptoms include:
Bleeding during bowel movements, often seen as bright red blood on toilet paper or in the stool.
Pain or discomfort around the anal area, particularly when sitting or during bowel movements.
Itching or irritation in the anal region.
Swelling or a lump near the anus.
While these symptoms can be indicative of hemorrhoids, they may also signal other health issues, so consulting a healthcare professional is advisable.
Additionally, lifestyle factors such as a low-fiber diet, prolonged sitting, or straining during bowel movements can exacerbate these symptoms. Incorporating dietary changes, such as increasing fiber intake through fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help alleviate symptoms and prevent future occurrences. Regular exercise and staying hydrated are also crucial components of maintaining bowel health and reducing the risk of developing hemorrhoids.
Causes of Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids can develop due to various factors, often related to increased pressure on the veins in the rectum. Understanding these causes can help in prevention and management.
Common Risk Factors
Several risk factors contribute to the development of hemorrhoids:
Chronic Constipation or Diarrhea: Straining during bowel movements can increase pressure on the veins.
Pregnancy: The weight of the fetus and hormonal changes can lead to swollen veins.
Obesity: Excess weight can put additional pressure on the rectum.
Aging: As individuals age, the tissues supporting the veins can weaken.
Awareness of these risk factors can guide individuals in adopting healthier habits to mitigate their risks. For instance, recognizing the signs of chronic constipation or diarrhea can prompt individuals to seek medical advice or make dietary adjustments.
Additionally, understanding that pregnancy can lead to temporary changes in the body can help expectant mothers take preventive measures, such as engaging in gentle exercise or consulting with healthcare providers about safe dietary choices.
Lifestyle Factors
Certain lifestyle choices can also contribute to the development of hemorrhoids:
Low Fiber Diet: A diet lacking in fiber can lead to constipation, increasing the risk of hemorrhoids.
Sitting for Extended Periods: Prolonged sitting, especially on the toilet, can increase pressure on the anal veins.
Lack of Physical Activity: Regular exercise helps promote healthy bowel function.
Making positive changes in these areas can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing hemorrhoids. For example, incorporating more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into one’s diet can enhance fiber intake, facilitating smoother bowel movements.
Similarly, breaking up long periods of sitting with short walks or stretches can alleviate pressure on the rectum. Engaging in regular physical activity not only supports digestive health but also contributes to overall well-being, making it an essential component of a proactive approach to hemorrhoid prevention.
Diagnosis of Hemorrhoids
Diagnosing hemorrhoids typically involves a physical examination and a review of the patient's medical history. Healthcare providers may use several methods to confirm the presence of hemorrhoids.
Physical Examination
A healthcare professional will often begin with a visual inspection of the anal area. This examination can reveal external hemorrhoids and any signs of irritation or swelling. For internal hemorrhoids, a digital rectal exam may be performed. During this exam, the doctor gently inserts a lubricated, gloved finger into the rectum to assess for any abnormalities, such as lumps or tenderness, which can indicate the presence of internal hemorrhoids.
Additional Diagnostic Tests
If necessary, further diagnostic tests may be conducted:
Anoscopy: A small tube is inserted into the anus to visualize the lower rectum.
Sigmoidoscopy or Colonoscopy: These procedures allow for a more comprehensive examination of the colon and rectum, particularly if bleeding is present.
These tests help rule out other conditions that may present similar symptoms, ensuring an accurate diagnosis. For instance, conditions such as anal fissures, rectal prolapse, or even colorectal cancer can mimic the symptoms of hemorrhoids.
Therefore, a thorough investigation is crucial, especially in patients experiencing significant pain or bleeding.
Additionally, healthcare providers may ask about lifestyle factors, such as diet and bowel habits, which can contribute to the development of hemorrhoids. A high-fiber diet, for example, can help alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrence, making dietary history an important aspect of the diagnostic process.
Treatment Options for Hemorrhoids
Treatment for hemorrhoids varies based on severity and symptoms. Options range from conservative home remedies to medical interventions.
Home Remedies
For mild cases, several home remedies can alleviate symptoms:
Warm Baths: Soaking in warm water can reduce discomfort and soothe the anal area.
Over-the-Counter Creams: Creams containing hydrocortisone can help reduce inflammation and itching.
Increased Fiber Intake: Consuming a diet rich in fiber can ease bowel movements and reduce straining.
These remedies can be effective for managing symptoms and preventing further complications.
Additionally, staying well-hydrated is crucial; drinking plenty of water can help soften stools and promote regular bowel movements, further alleviating the pressure on hemorrhoids. Incorporating foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into your diet not only enhances fiber intake but also contributes to overall digestive health. Regular exercise can also play a role in preventing constipation, which is a common trigger for hemorrhoids.
Medical Treatments
If home remedies are ineffective, medical treatments may be necessary:
Minimally Invasive Procedures: Techniques such as rubber band ligation or sclerotherapy can treat hemorrhoids without the need for surgery.
Surgical Options: In severe cases, a hemorrhoidectomy may be performed to remove hemorrhoids surgically.
Consultation with a healthcare provider can help determine the most appropriate treatment based on individual circumstances. In some cases, doctors may recommend lifestyle changes alongside medical treatments, such as avoiding prolonged sitting or standing, which can exacerbate symptoms.
Furthermore, understanding the underlying causes of hemorrhoids, such as pregnancy or chronic constipation, can aid in developing a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both symptoms and root causes. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare professional can ensure that the chosen treatment remains effective and allows for adjustments as needed.
Prevention of Hemorrhoids
 Preventing hemorrhoids is often achievable through lifestyle modifications and awareness of risk factors. Here are some effective strategies:
Preventing hemorrhoids is often achievable through lifestyle modifications and awareness of risk factors. Here are some effective strategies:
Dietary Changes
Adopting a high-fiber diet can significantly reduce the risk of hemorrhoids. Foods rich in fiber include:
Fruits and vegetables
Whole grains
Legumes
Increased fluid intake is also essential to help soften stool, making it easier to pass. Aim for at least eight glasses of water a day, and consider incorporating herbal teas and broths, which can also contribute to hydration.
Additionally, certain fruits like prunes and pears are particularly effective due to their natural laxative properties, promoting healthy digestion and regularity.
Healthy Bowel Habits
Practicing good bowel habits can prevent straining:
These habits can help maintain regular bowel function and reduce the risk of hemorrhoids.
Furthermore, incorporating gentle exercise into your daily routine, such as walking or yoga, can stimulate bowel movements and improve overall digestive health. Engaging in regular physical activity not only helps to prevent constipation but also enhances circulation, which is crucial for preventing the swelling of veins that can lead to hemorrhoids.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While hemorrhoids are common, certain symptoms warrant prompt medical attention. These include:
Severe pain or discomfort that does not improve with home remedies.
Persistent bleeding, especially if it is heavy or accompanied by other symptoms.
Changes in bowel habits or stool consistency.
Consulting a healthcare professional can help rule out more serious conditions and provide appropriate treatment. Doctronic.ai is your AI-powered health assistant supported by real medical experts. Get personalized guidance and alternative treatments tailored to your needs, with expert insights backed by data and delivered with care.
It is important to note that while hemorrhoids can often be managed with over-the-counter treatments and lifestyle changes, symptoms that persist or worsen may indicate complications such as thrombosed hemorrhoids, which can lead to increased pain and swelling. In such cases, medical intervention may be necessary to alleviate symptoms and prevent further issues.
Additionally, individuals experiencing significant changes in their bowel habits should be particularly vigilant. Conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease or colorectal cancer can present with symptoms similar to those of hemorrhoids.
Therefore, it is crucial to communicate any accompanying symptoms, such as unexplained weight loss, fatigue, or changes in appetite, during your medical consultation. Early detection and diagnosis are key to effective treatment and management of any underlying conditions.
Need Help Identifying Hemorrhoids? Doctronic Can Help!
Understanding the differences between a normal anus and hemorrhoids is vital for maintaining digestive health. Awareness of symptoms, causes, and treatment options empowers individuals to take proactive steps in managing their health. By adopting preventive measures and seeking timely medical advice, individuals can reduce their risk of developing hemorrhoids and ensure a better quality of life.
Are you wondering if it's normal or a sign of hemorrhoids? Knowing the signs can help you take action early to protect your health. Doctronic will help you learn about symptoms, prevention, and treatment options for hemorrhoids—take control of your well-being today!



 The human body is a
The human body is a  Preventing hemorrhoids is often achievable through lifestyle modifications and awareness of risk factors. Here are some effective strategies:
Preventing hemorrhoids is often achievable through lifestyle modifications and awareness of risk factors. Here are some effective strategies: