IUD vs Implant: Which Birth Control Option Is Right for You?
Choosing Between IUD and Implant: What You Need to KnowWhen it comes to long-term birth control, two popular options are the intrauterine device (IUD) and the contraceptive [...]
Read More
Medically reviewed by Alan Lucks | MD, Alan Lucks MDPC Private Practice - New York on December 19th, 2025.
Understand the differences between IUDs and implants, including how they work and their effectiveness.
Explore the pros and cons of each method to find what fits your lifestyle and health needs.
Learn about the insertion process, side effects, and duration of protection for both options.
Discover how telehealth services like Doctronic.ai can help you access expert medical advice and convenient care.
When it comes to long-term birth control, two popular options are the intrauterine device (IUD) and the contraceptive implant. Both provide effective, low-maintenance contraception but differ in how they work, how they’re placed, and how long they last. Understanding these differences can help you decide which fits your health, lifestyle, and preferences best.
Both methods are highly effective, with failure rates under 1%, making them among the most reliable reversible birth control options available. However, the choice often comes down to personal comfort with the procedure, hormone preferences, and side effect profiles. Some individuals may prefer the IUD due to its long-term effectiveness without the need for daily attention, while others may lean toward the implant for its ease of insertion and removal.
An IUD is a small, T-shaped device inserted into the uterus by a healthcare provider. There are two main types:
Hormonal IUDs release a progestin hormone that thickens cervical mucus and thins the uterine lining, preventing sperm from reaching or fertilizing an egg.
Copper IUDs use copper to create an environment toxic to sperm, blocking fertilization without hormones.
Depending on the type, an IUD can protect against pregnancy for 3 to 12 years. The hormonal IUD may also lead to lighter periods or even amenorrhea (the absence of menstruation) for some users, which can be a significant advantage for those who experience heavy or painful periods. On the other hand, the copper IUD does not alter menstrual cycles and may even cause heavier bleeding and cramping initially, making it essential for users to weigh their options carefully based on their menstrual health.
The contraceptive implant is a small, flexible rod about the size of a matchstick inserted just under the skin of the upper arm. It releases a steady dose of progestin hormone to prevent ovulation and thicken cervical mucus. The implant provides protection for up to 3 years. One of the significant benefits of the implant is its convenience; once it’s in place, there’s nothing to remember daily, and it can be easily removed by a healthcare provider when you decide to conceive or switch methods.
The implant can be a suitable option for individuals who prefer a hormone-based method without the risk of estrogen-related side effects, as it contains only progestin. However, some users may experience side effects such as irregular bleeding, headaches, or mood changes, which can vary significantly from person to person. It’s crucial to discuss these potential side effects with a healthcare provider to ensure that the chosen method aligns with individual health needs and lifestyle preferences.
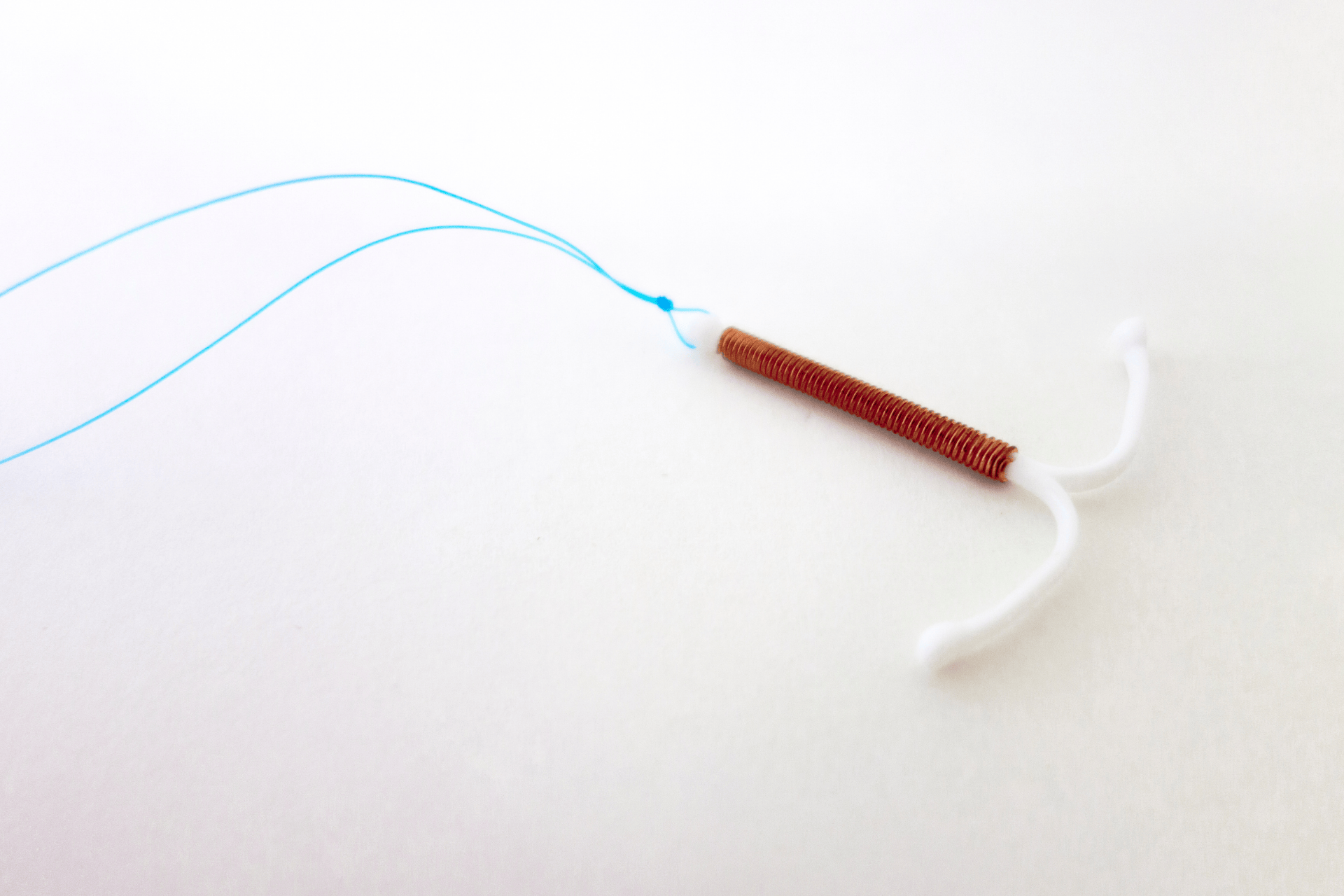 Insertion and Removal: What to Expect
Insertion and Removal: What to ExpectInsertion involves a brief office visit where a healthcare provider places the device inside the uterus. The procedure can cause some discomfort or cramping, but it is usually quick. After insertion, you might experience spotting or irregular periods for a few months.
Removal is also done by a healthcare professional and is generally straightforward. Fertility returns quickly after removal.
The implant is inserted under local anesthesia in a quick outpatient procedure. You might feel some soreness or bruising around the site afterward. Removal is similarly simple and done in a healthcare setting. Once removed, fertility returns rapidly.
Long-lasting protection, up to 12 years for some types.
Choice between hormonal and non-hormonal options.
Low maintenance after insertion.
Hormonal IUDs may reduce heavy menstrual bleeding.
Insertion can be uncomfortable or painful for some.
Possible side effects include spotting, cramping, or heavier periods (especially with copper IUDs).
Rare risks include expulsion or uterine perforation.
Highly effective and discreet.
Lasts up to 3 years with no daily attention needed.
May reduce menstrual bleeding and cramps.
Easy to remove when desired.
It can cause irregular bleeding or spotting.
May lead to hormonal side effects like mood changes or acne.
Requires a minor procedure for insertion and removal.
Choosing between an IUD and an implant depends on your preferences for hormone use, how long you want protection, and your comfort with the insertion process. If you prefer a hormone-free option or want protection for a decade, a copper IUD might be ideal. If you want a hormone-based method that’s discreet and lasts a few years, the implant could be a better fit.
Consider your tolerance for potential side effects and how you feel about the insertion procedure. Talking with a healthcare provider can help clarify what suits your health history and lifestyle.
Accessing expert advice has never been easier thanks to telehealth platforms like Doctronic.ai. You can get personalized consultations, ask questions about birth control options, and receive treatment recommendations-all from the comfort of your home.
Doctronic’s AI-powered service offers fast, comprehensive answers based on the latest medical research. It remembers your health history to provide tailored guidance, helping you make informed decisions about contraception. For those seeking convenient telehealth video visits with licensed doctors, Doctronic also offers affordable appointments available 24/7 nationwide.
Fertility typically returns quickly after removing either an IUD or an implant. Many people conceive within a few months if they stop using birth control.
Yes. Both methods are safe and effective for people who have never been pregnant, but your healthcare provider will assess your individual health factors.
Both IUDs and implants are generally safe. Rare risks include infection or device expulsion with IUDs and minor complications at the implant site. Your provider will discuss these before insertion.
Yes, switching is possible. You can have one removed and the other inserted during the same visit if appropriate.
Both IUDs and implants offer reliable, long-lasting contraception with minimal daily effort. The best choice depends on your personal preferences, medical history, and how you feel about hormones and procedures.
Using a trusted telehealth service like Doctronic.ai can simplify the process of getting expert advice and scheduling appointments. With over 10 million users, Doctronic combines AI-driven medical expertise with compassionate care to help you find the right birth control option and manage your health confidently.
Both methods have failure rates below 1%, making them among the most effective reversible birth control options.
Yes, both require evaluation and insertion by a healthcare provider. Telehealth services like Doctronic.ai can help guide you through the process.
Hormonal IUDs and implants often reduce or stop periods over time, but some people experience irregular bleeding initially. Copper IUDs may increase menstrual bleeding and cramps.
You can have your IUD or implant removed at any time, and fertility usually returns quickly.
Most medications do not affect IUDs or implants, but some enzyme-inducing drugs may reduce hormonal effectiveness. Consult your healthcare provider for specifics.
Choosing Between IUD and Implant: What You Need to KnowWhen it comes to long-term birth control, two popular options are the intrauterine device (IUD) and the contraceptive [...]
Read More