Understanding Ingrown Hairs
Ingrown hairs occur when a hair grows back into the skin instead of rising up from it. This can lead to irritation, inflammation, and sometimes infection. They are most commonly seen in areas where hair is frequently shaved or waxed, such as the face, neck, and bikini line.
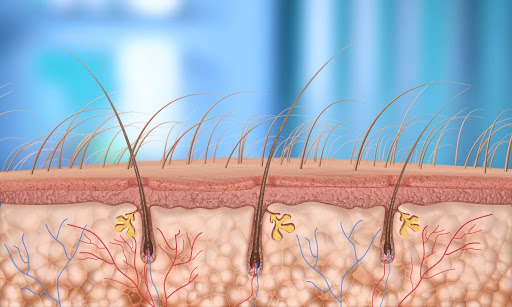 The condition can affect anyone, but it is particularly prevalent among individuals with curly or coarse hair. Ingrown hairs can be more than just a cosmetic concern; they can also cause significant discomfort and emotional distress, particularly for those who experience them frequently.
The condition can affect anyone, but it is particularly prevalent among individuals with curly or coarse hair. Ingrown hairs can be more than just a cosmetic concern; they can also cause significant discomfort and emotional distress, particularly for those who experience them frequently.
Many people may not realize that ingrown hairs can also occur in areas where hair is not typically shaved, such as the legs or underarms. This is particularly true for individuals who may have sensitive skin or are prone to other skin conditions.
Additionally, ingrown hairs can sometimes lead to hyperpigmentation, where the skin darkens in response to inflammation, leaving behind marks that can take time to fade. Understanding the underlying causes and recognizing the symptoms early can help manage and prevent this common issue.
Causes of Ingrown Hairs
Several factors contribute to the development of ingrown hairs. The most common causes include:
Improper shaving techniques, such as shaving against the grain.
Wearing tight clothing can irritate the skin.
Hair texture and growth patterns, particularly in curly hair.
Skin conditions that cause inflammation or block hair follicles.
In addition to these factors, the use of dull razors can exacerbate the problem, as they may not cut the hair cleanly, leading to sharper edges that are more likely to penetrate the skin.
Furthermore, exfoliating the skin can help prevent ingrown hairs by removing dead skin cells that can clog hair follicles. Regular exfoliation, combined with proper shaving techniques, can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing ingrown hairs, making it an essential part of any grooming routine.
Symptoms and Signs
Ingrown hairs can manifest in various ways, often leading to discomfort. Common symptoms include:
Red, swollen bumps on the skin.
Itching or tenderness in the affected area.
Pus-filled blisters in more severe cases.
In some instances, ingrown hairs can become infected, leading to more serious symptoms requiring medical attention. The presence of pus-filled blisters may indicate an infection, which can be accompanied by increased pain and swelling.
If left untreated, these infections can lead to scarring or more severe dermatological issues. Therefore, it's crucial to monitor any ingrown hairs closely and seek professional advice if symptoms worsen or do not improve with home remedies.
Taking proactive steps, such as using antiseptic treatments or consulting a dermatologist, can help manage the condition effectively and prevent further complications.
Understanding Herpes
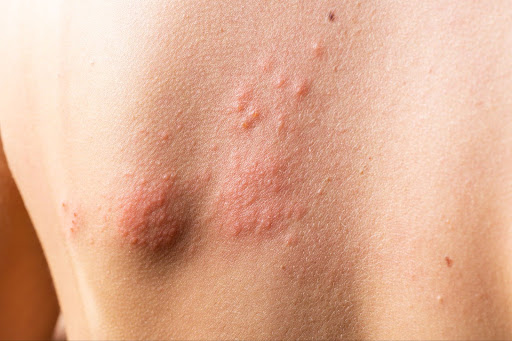 Herpes is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), which has two main types: HSV-1 and HSV-2. HSV-1 primarily causes oral herpes, resulting in cold sores, while HSV-2 is typically associated with genital herpes.
Herpes is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), which has two main types: HSV-1 and HSV-2. HSV-1 primarily causes oral herpes, resulting in cold sores, while HSV-2 is typically associated with genital herpes.
This condition is highly contagious and can be transmitted through direct contact with an infected individual. The prevalence of herpes is significant, with millions of people worldwide carrying the virus, often without even realizing it.
This widespread nature of the virus underscores the importance of awareness and education regarding its transmission and management.
Transmission and Risk Factors
Herpes is transmitted through skin-to-skin contact, and several factors can increase the risk of contracting the virus:
Engaging in unprotected sexual activity.
Having multiple sexual partners.
Weakened immune systems due to illness or stress.
It is important to note that herpes can be transmitted even when an infected person does not have visible symptoms. Asymptomatic shedding, where the virus is present on the skin without any visible sores, can occur, making it crucial for individuals to communicate openly with their partners about their sexual health.
Additionally, using barriers such as condoms can significantly reduce the risk of transmission, although they do not eliminate it.
Symptoms and Signs
The symptoms of herpes can vary significantly from person to person. Some may experience mild symptoms, while others may have more severe outbreaks. Common signs include:
Painful blisters or sores in the affected area.
Itching or burning sensations.
Flu-like symptoms, including fever and swollen lymph nodes.
Various factors, such as stress, illness, or hormonal changes, can trigger herpes outbreaks. Understanding these triggers can help individuals manage their condition more effectively.
For instance, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including proper nutrition, regular exercise, and stress management techniques, can reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks.
Furthermore, antiviral medications may be prescribed to help control symptoms and decrease the likelihood of transmission, allowing those affected to lead a more normal life while managing their condition.
Similarities Between Ingrown Hairs and Herpes
At first glance, ingrown hairs and herpes may appear to have some similarities, particularly in their symptoms. Both conditions can cause discomfort and visible skin changes. However, understanding the distinction between the ingrown hair vs herpes debate is essential to ensure proper treatment and effective management.
Common Symptoms
Both ingrown hairs and herpes can present with:
Redness and swelling in the affected area.
Itching or irritation that can lead to scratching.
Potential for secondary infections if left untreated.
These overlapping symptoms can sometimes lead to confusion, making it crucial to understand the underlying causes of each condition. For instance, ingrown hairs occur when hair grows back into the skin instead of out of the follicle, often due to improper shaving techniques or coarse hair texture.
In contrast, herpes is caused by the herpes simplex virus, which can remain dormant in the body and reactivate, leading to outbreaks. Understanding these distinctions can help individuals seek the proper treatment and avoid unnecessary anxiety.
Potential for Infection
Both conditions can become infected if not appropriately managed. Ingrown hairs can lead to folliculitis, an infection of the hair follicle, while herpes sores can become infected with bacteria if they are scratched or improperly cared for. In both cases, seeking medical advice is advisable if symptoms worsen or do not improve.
Additionally, it’s important to note that while ingrown hairs are typically localized and can often be treated at home with proper hygiene and care, herpes requires a more comprehensive approach, including antiviral medications to manage outbreaks and reduce transmission risk.
This distinction highlights the importance of understanding the nature of each condition to ensure effective treatment and minimize complications.
Key Differences Between Ingrown Hairs and Herpes
Despite their similarities, ingrown hair vs herpes highlights two fundamentally different conditions. Understanding these differences is crucial for accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and long-term management.
Nature of the Condition
Ingrown hairs are primarily a physical condition resulting from hair growth patterns and shaving techniques, while herpes is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. This distinction is critical when considering treatment options:
Duration and Recurrence
Ingrown hairs typically resolve on their own or with minor intervention within a few days to weeks. In contrast, herpes is a chronic condition that can lead to recurrent outbreaks throughout a person's life.
The frequency and severity of these outbreaks can vary widely among individuals. Factors such as stress, illness, and hormonal changes can trigger these episodes, making it essential for those affected to recognize their triggers and manage their health accordingly.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis for ingrown hairs is usually straightforward and can often be made through physical examination. Treatment may include:
Warm compresses to reduce inflammation.
Topical creams to soothe the skin.
Proper shaving techniques to prevent recurrence.
Herpes, on the other hand, may require laboratory testing to confirm the presence of the virus. Treatment options often include:
Antiviral medications like acyclovir or valacyclovir.
Topical creams to alleviate symptoms during outbreaks.
Preventative measures to reduce the risk of transmission.
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle adjustments can also significantly contribute to managing both conditions. For ingrown hairs, adopting a routine that includes gentle exfoliation can help prevent hair from becoming trapped beneath the skin.
This can be particularly beneficial for those with curly or coarse hair types, who are more prone to ingrown hairs.
Meanwhile, individuals dealing with herpes may find that maintaining a healthy immune system through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques can help reduce the frequency of outbreaks.
Moreover, open communication with partners about the condition is vital for managing relationships and ensuring both parties are informed about health risks.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Knowing when to seek medical help is essential for both conditions. While ingrown hairs can often be managed at home, certain signs warrant a doctor's visit:
If the area becomes increasingly painful or swollen.
If there is pus or other signs of infection.
If the ingrown hair does not improve with home treatment.
For herpes, medical attention should be sought if:
Symptoms are severe or recurrent.
There are concerns about transmission to partners.
New or unusual symptoms develop.
In addition to these signs, it is important to monitor any changes in the affected areas. For ingrown hairs, if you notice the development of a hard lump or a cyst, this could indicate a more serious issue that requires professional evaluation.
Furthermore, if you have a history of skin conditions or if you are prone to developing infections, it is wise to consult a healthcare provider sooner rather than later. Early intervention can prevent complications and promote faster healing, allowing you to return to your regular activities without discomfort.
Similarly, with herpes, understanding the full scope of the condition is crucial. If you experience flu-like symptoms, such as fever or swollen lymph nodes, alongside the typical sores, this could signify a more extensive outbreak that necessitates medical intervention.
Additionally, discussing your symptoms openly with a healthcare professional can provide you with valuable insights into managing the condition effectively and reducing the risk of transmission.
They can also guide you on the best preventive measures to take, safeguarding your health and that of your partners.
Preventive Measures
Preventive strategies can manage both ingrown hairs and herpes. Understanding these measures can help reduce the risk of developing either condition.
Preventing Ingrown Hairs
To minimize the risk of ingrown hairs, consider the following tips:
Use proper shaving techniques, such as shaving in the direction of hair growth.
Exfoliate the skin regularly to remove dead skin cells that can block hair follicles.
Avoid tight clothing that may irritate the skin.
Additionally, using a sharp razor and replacing it frequently can significantly reduce the chances of hair getting trapped under the skin. Many people find that incorporating a soothing aftershave or moisturizing lotion can help calm the skin post-shave, reducing irritation and promoting healthier hair growth.
For those prone to ingrown hairs, considering alternative hair removal methods, such as laser hair removal or waxing, may provide a longer-term solution, as these methods can prevent hair from growing back in a way that leads to ingrowth.
Preventing Herpes Outbreaks
To reduce the risk of herpes outbreaks and transmission, individuals can:
Practice safe sex by using condoms or dental dams.
Limit the number of sexual partners.
Manage stress and maintain a healthy lifestyle to support the immune system.
Moreover, monitoring potential triggers, such as certain foods or emotional stressors, can be beneficial in managing the condition. Some individuals find that taking antiviral medications as prescribed by a healthcare provider can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks.
Staying hydrated and ensuring adequate sleep are also crucial components of a strong immune system, which can help fend off potential flare-ups. Engaging in regular exercise not only contributes to overall health but can also alleviate stress, further minimizing the likelihood of an outbreak.
Let Doctronic Diagnose the Difference
Ingrown hair or herpes? Don’t play the guessing game. AI doctor Doctronic delivers accurate, expert-level guidance to help you understand what’s going on. Because real answers mean real peace of mind.



 The condition can affect anyone, but it is particularly prevalent among individuals with curly or coarse hair. Ingrown hairs can be more than just a cosmetic concern; they can also cause significant discomfort and emotional distress, particularly for those who experience them frequently.
The condition can affect anyone, but it is particularly prevalent among individuals with curly or coarse hair. Ingrown hairs can be more than just a cosmetic concern; they can also cause significant discomfort and emotional distress, particularly for those who experience them frequently. Herpes is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), which has two main types: HSV-1 and HSV-2. HSV-1 primarily causes oral herpes, resulting in cold sores, while HSV-2 is typically associated with genital herpes.
Herpes is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), which has two main types: HSV-1 and HSV-2. HSV-1 primarily causes oral herpes, resulting in cold sores, while HSV-2 is typically associated with genital herpes.