Vaginal Dryness During Menopause
Meta Description: Understand why vaginal dryness during menopause occurs and explore effective treatments, from moisturizing therapies to low-dose estrogen and laser [...]
Read More
Medically reviewed by Oghenefejiro Okifo | MD, Harvard Medical School | Henry Ford Hospital - Detroit, MI on May 16th, 2025.
Bacterial spread from dental pulp to surrounding tissues typically occurs within 3-7 days, with progression to sepsis possible in 1-2 weeks depending on immune status and bacterial virulence.
Upper jaw infections carry higher mortality risk because venous drainage connects directly to brain sinuses, potentially causing cavernous sinus thrombosis within 24-48 hours of facial swelling.
Ludwig's angina—infection spreading to the floor of the mouth—can cause airway obstruction requiring emergency intubation, with symptoms progressing rapidly over 12-24 hours.
Immunocompromised patients, diabetics, and those over 65 face accelerated timelines, with systemic complications developing 2-3 times faster than in healthy adults.
Temperature above 101°F (38.3°C), difficulty swallowing, or neck stiffness indicate potential spread to deep fascial spaces requiring immediate IV antibiotics and possible surgical drainage.
A tooth infection, also known as a dental abscess, occurs when bacteria invade the tooth's pulp, leading to inflammation and pus formation.
While many may dismiss a toothache as a minor inconvenience, the reality is that untreated dental infections can escalate into serious health risks.
In severe cases, people even wonder how long until a tooth infection kills you, a stark reminder of why prompt treatment is so important. Understanding the timeline and potential consequences of ignoring a tooth infection is crucial for maintaining overall health.
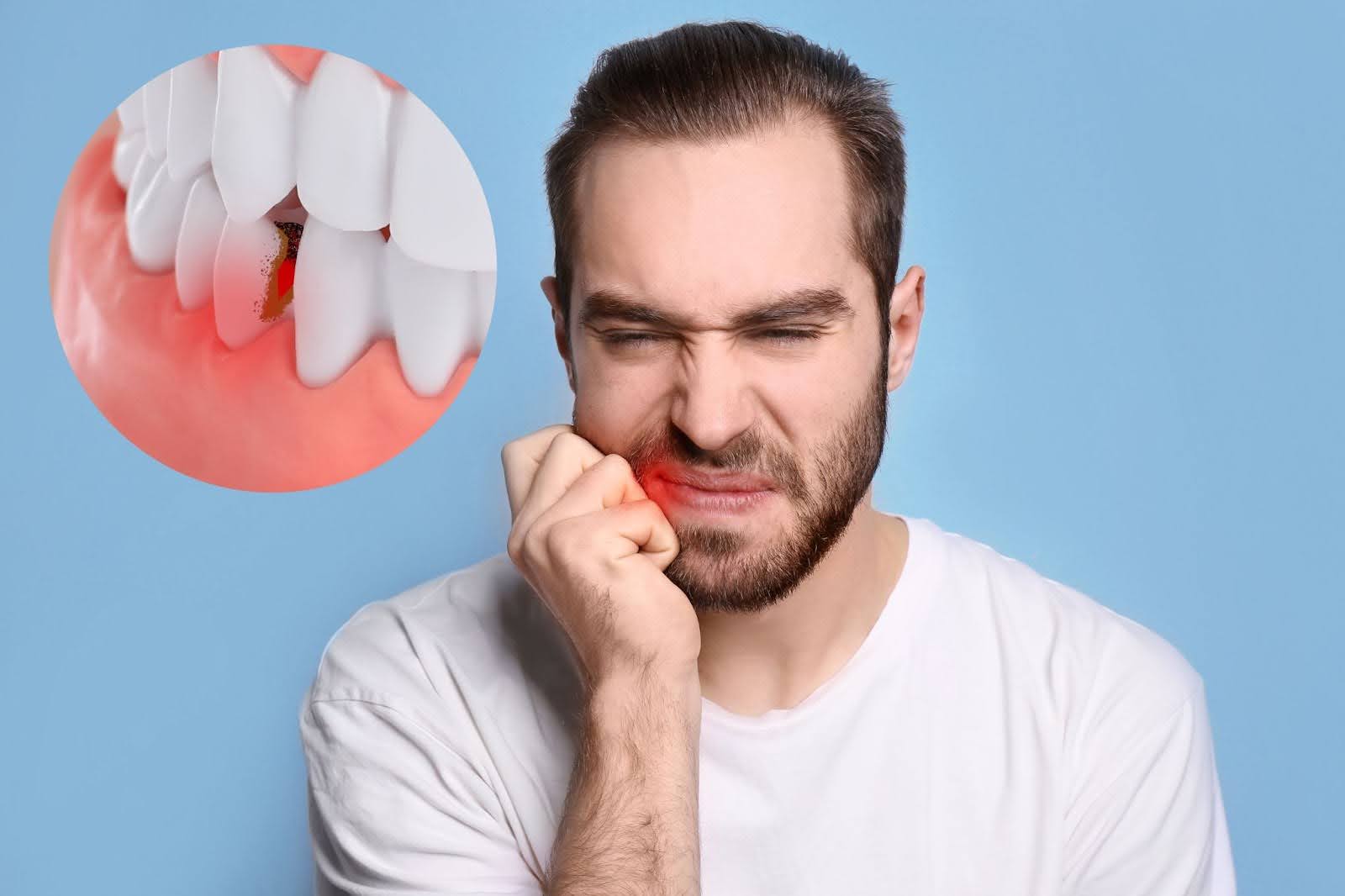
Tooth infections typically arise from untreated cavities, gum disease, or dental trauma. When the protective enamel of a tooth is compromised, bacteria can penetrate deeper into the tooth structure, reaching the pulp.
This invasion leads to inflammation and the formation of pus, resulting in pain and swelling.
Several factors can contribute to the development of a tooth infection, including:
Poor oral hygiene
Diet high in sugar
Existing dental issues
Weakened immune system
Additionally, certain lifestyle choices can exacerbate the risk of tooth infections. For instance, tobacco use not only weakens the immune response but also contributes to gum disease, creating an environment conducive to bacterial growth.
Furthermore, individuals who frequently consume acidic beverages, such as sodas and fruit juices, may experience enamel erosion, making their teeth more susceptible to decay and subsequent infection.
Regular dental check-ups are crucial, as they can help identify early signs of decay or gum disease before they escalate into more serious infections.
For added peace of mind between visits, you can also consult Doctronic’s free AI doctor to assess symptoms and get quick, reliable insights.
Recognizing the symptoms of a tooth infection is vital for timely intervention. Common signs include:
Severe toothache that may radiate to the jaw or ear
Swelling in the gums or face
Fever and general malaise
Bad breath or a foul taste in the mouth
In addition to these symptoms, some individuals may experience difficulty in chewing or biting down on food, as the pressure can exacerbate the pain.
The presence of a visible abscess, which appears as a swollen bump on the gums, is another alarming sign that indicates the need for immediate dental attention. If any of these symptoms are present, seeking dental care promptly is essential to prevent further complications.
Untreated infections can lead to more severe health issues, including the spread of bacteria to other parts of the body, which can result in systemic infections.
Therefore, being vigilant about oral health and addressing any discomfort early on can make a significant difference in overall well-being.
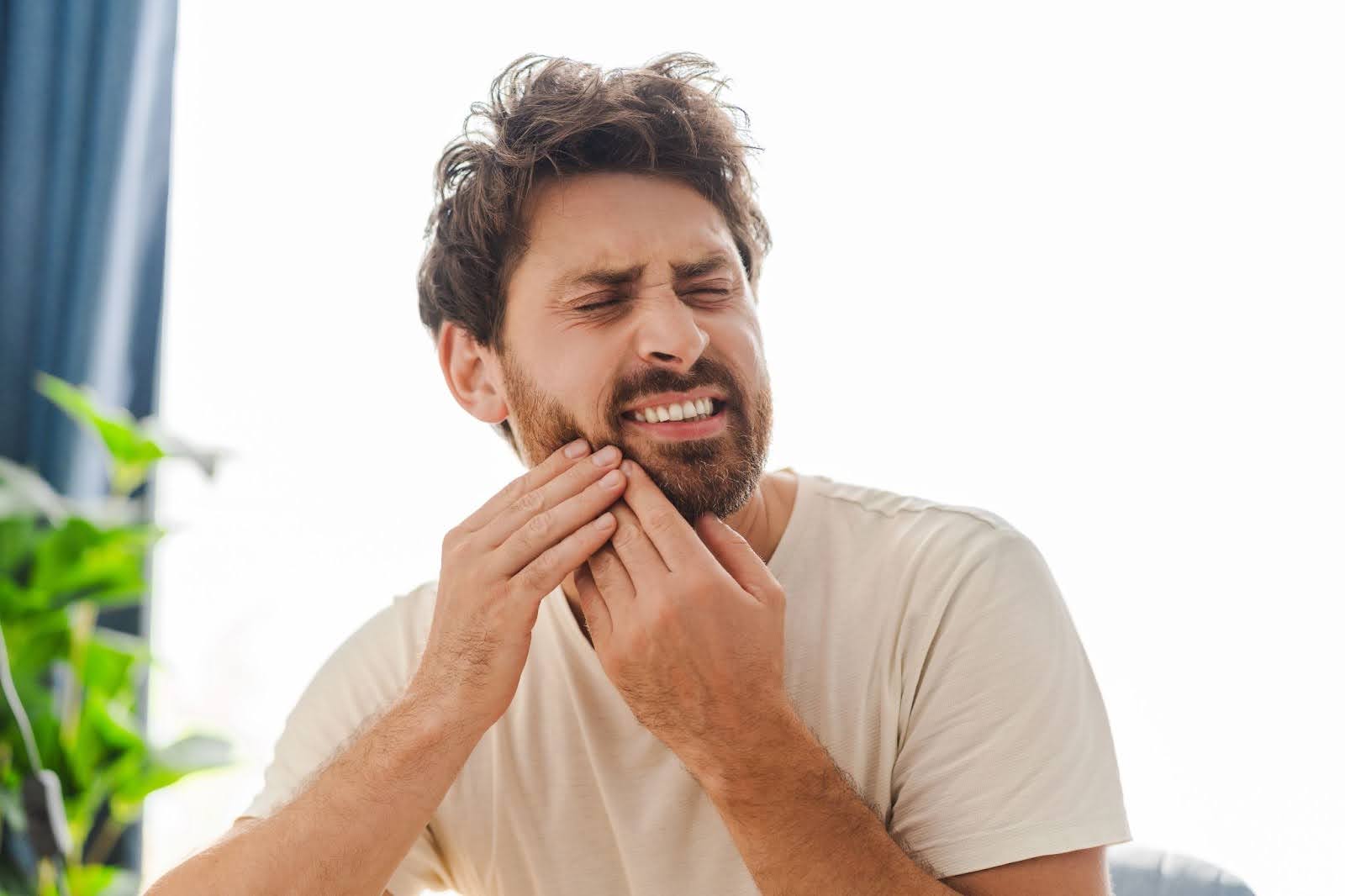

In the early stages of a tooth infection, symptoms may be mild and easily overlooked. Individuals might experience a dull ache or sensitivity to hot and cold stimuli.
At this point, the infection is localized, and while uncomfortable, it may not pose an immediate threat to overall health.
Many people may dismiss these initial signs as a mere inconvenience, attributing the discomfort to something as simple as a cavity or minor gum irritation. However, it is crucial to pay attention to these early warning signs, as they can indicate the beginning of a more serious issue.
However, as the infection progresses, the pain typically intensifies, and swelling may become more pronounced. This escalation is a clear signal that professional dental intervention is necessary.
The discomfort can evolve into sharp, throbbing pain that radiates to the jaw or ear, making it difficult to eat or speak. Additionally, patients may notice an unpleasant taste in their mouth or bad breath, which can be attributed to the pus that forms as the body attempts to fight off the infection.
Ignoring these symptoms can lead to a cycle of worsening pain and potential systemic effects, emphasizing the need for timely dental care.
If left untreated, a tooth infection can lead to more serious complications. The bacteria can spread beyond the tooth and into the surrounding tissues, leading to conditions such as:
Periodontal abscess
Osteomyelitis (bone infection)
Sepsis (a life-threatening response to infection)
Each of these conditions can have severe consequences, underscoring the importance of addressing a tooth infection promptly. For instance, a periodontal abscess can cause significant damage to the supporting structures of the teeth, potentially leading to tooth loss.
Osteomyelitis, on the other hand, can result in chronic pain and may require surgical intervention to remove infected bone tissue.
Sepsis, being a systemic response, can lead to organ failure and requires immediate medical attention, often necessitating hospitalization and aggressive treatment.
The risk of these complications highlights the critical nature of seeking dental care at the first sign of infection, as early intervention can prevent a cascade of health issues that extend far beyond the mouth.
The timeline for a tooth infection to become life-threatening can vary significantly based on several factors, including the individual's overall health, the severity of the infection, and the presence of underlying medical conditions.
Generally, an untreated tooth infection can progress to serious complications within a few days to a couple of weeks.
In some cases, the infection may remain localized for an extended period, but this does not mean it is safe to ignore it. The risk of systemic complications increases the longer the infection is left untreated.
For instance, a localized abscess may initially cause only mild discomfort, but as bacteria proliferate, they can infiltrate surrounding tissues, leading to more severe pain and swelling. This progression can also result in fever and malaise, indicating that the body is fighting an infection.
Several factors can influence how quickly a tooth infection escalates, including:
Immune System Health: Individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those with diabetes or undergoing chemotherapy, may experience faster progression.
Location of the Infection: Infections in the upper jaw can potentially spread to the brain, while those in the lower jaw may affect the neck and throat.
Type of Bacteria: The virulence of the bacteria involved can also significantly affect how quickly the infection spreads.
Moreover, lifestyle factors such as smoking and poor oral hygiene can exacerbate the situation, leading to a more rapid deterioration of dental health.
Smoking, in particular, impairs blood flow and can hinder the healing process, allowing infections to thrive. Additionally, neglecting regular dental check-ups can result in undiagnosed cavities or gum disease, which can serve as breeding grounds for bacteria.
Understanding these factors is crucial for individuals to recognize the importance of early intervention and the potential consequences of delaying treatment.
Furthermore, the symptoms associated with a tooth infection can vary widely. While some individuals may experience sharp pain or swelling, others might notice a persistent bad taste in their mouth or difficulty swallowing.
These symptoms can serve as warning signs that should not be overlooked. Awareness of these risks can motivate individuals to seek dental care promptly, ensuring that minor issues do not escalate into major health concerns.
As a tooth infection progresses, it can lead to various local complications. These include:
Abscess Formation: Pockets of pus can form in the gums or jaw, leading to severe pain and swelling. This localized infection can create a throbbing sensation, making it difficult to eat or even speak comfortably. In some cases, the abscess may burst, releasing pus into the mouth, which can provide temporary relief but also increases the risk of spreading the infection further.
Bone Loss: The infection can erode the bone surrounding the tooth, potentially leading to tooth loss. This loss of bone density can not only affect the stability of adjacent teeth but also complicate future dental procedures, such as implants or bridges, which rely on a healthy bone structure for support.
Sinus Infection: Infections in the upper teeth can spread to the sinuses, causing sinusitis. Symptoms may include facial pain, nasal congestion, and fever, which can mimic other illnesses. The connection between dental health and sinus issues underscores the importance of addressing tooth infections promptly to prevent further complications.
In more severe cases, the bacteria from a tooth infection can enter the bloodstream, leading to systemic complications. These may include:
Sepsis: A life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes widespread inflammation. Symptoms of sepsis can escalate quickly, including fever, rapid heart rate, and confusion, necessitating immediate medical intervention to prevent organ failure.
Endocarditis: An infection of the inner lining of the heart, which can occur if bacteria enter the bloodstream and settle in the heart. This condition can lead to serious complications, such as heart valve damage, and may require prolonged antibiotic treatment or even surgery to repair the affected valves.
Pneumonia: Aspiration of infected material can lead to lung infections. This risk is particularly heightened in individuals with compromised immune systems or those who have difficulty swallowing, as the bacteria can easily travel to the lungs, leading to a severe respiratory condition that may require hospitalization.
It is crucial to be vigilant for signs that a tooth infection may be becoming life-threatening. Symptoms that warrant immediate medical attention include:
Rapid swelling of the face or neck
Difficulty breathing or swallowing
High fever (over 101°F or 38.3°C)
Confusion or disorientation
In addition to these alarming symptoms, one should also be aware of persistent pain that escalates in intensity.
This pain may radiate to other areas such as the jaw, ear, or even the head, indicating that the infection is spreading beyond the initial site.
Furthermore, if there is a noticeable change in the color of the gums surrounding the infected tooth, such as increased redness or the presence of pus, these are also critical signs that should not be ignored.
The body's immune response can sometimes mask symptoms, but if you notice any unusual changes in your oral health, it’s imperative to consult a healthcare professional.
If any of the above symptoms occur, it is essential to seek emergency medical care. Delaying treatment in these situations can lead to severe consequences, including hospitalization or even death.
Infections can spread rapidly, especially if they reach the bloodstream, leading to sepsis, a life-threatening condition that requires immediate intervention.
Moreover, dental infections can also lead to complications such as abscess formation, which may necessitate surgical drainage or even tooth extraction.
It is important to remember that timely intervention can significantly alter the outcome, so erring on the side of caution is always advisable when it comes to dental health.
Maintaining good oral hygiene is the most effective way to prevent tooth infections. Key practices include:
Brushing teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste
Flossing daily to remove plaque between teeth
Regular dental check-ups and cleanings
A balanced diet plays a significant role in oral health. Limiting sugary snacks and beverages can reduce the risk of cavities, which are a primary cause of tooth infections. Incorporating foods rich in vitamins and minerals, such as:
Dairy products for calcium
Fruits and vegetables for vitamins
Nuts and seeds for healthy fats
When a tooth infection is diagnosed, prompt treatment is essential. Dental professionals may recommend several treatment options, including:
Antibiotics: To eliminate the bacterial infection.
Drainage: In cases of abscess, drainage of pus may be necessary to relieve pressure and pain.
Root Canal Therapy: To remove infected pulp and save the tooth.
Extraction: In severe cases, the affected tooth may need to be removed.
While awaiting professional treatment, individuals can manage symptoms with home care strategies such as:
Over-the-counter pain relievers to alleviate discomfort
Warm saltwater rinses to reduce swelling
Cold compresses to minimize pain and swelling
Tooth infections are not to be taken lightly. Ignoring the symptoms can lead to serious and potentially life-threatening complications.
Timely intervention is crucial for preventing the progression of an infection and safeguarding overall health. Regular dental check-ups, good oral hygiene, and prompt attention to dental issues can significantly reduce the risk of developing a tooth infection.
Always consult a dental professional if there are concerns about oral health, and for quick guidance before your appointment, a free AI doctor visit with Doctronic can help point you in the right direction.
Dental infections can become life-threatening within days, especially when affecting the upper jaw or in vulnerable populations, making early intervention critical. Seek emergency care immediately for high fever, breathing problems, or rapid facial swelling. If you're experiencing concerning symptoms from a tooth infection, Doctronic can help you determine the appropriate level of care needed.
Meta Description: Understand why vaginal dryness during menopause occurs and explore effective treatments, from moisturizing therapies to low-dose estrogen and laser [...]
Read MoreMeta Description: Discover why perimenopause causes itching and explore effective relief strategies, from hormone therapy to skincare tips, to soothe dry and itchy skin.When [...]
Read MoreMeta Description: Understand why weight gain during perimenopause occurs and learn how to manage it through protein intake, resistance training, and better sleep habits.Why [...]
Read More