
Understanding the causes of anal pain is essential for effective treatment. Two common conditions that can lead to significant discomfort are hemorrhoids and anal fissures. While they may share some symptoms, their causes, treatments, and implications differ markedly. This article will delve into the characteristics of each condition, helping to clarify the differences and guide individuals toward appropriate care.
Understanding Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, are swollen veins in the lower rectum and anus. They can be classified into two main types: internal and external. Internal hemorrhoids are located inside the rectum, while external hemorrhoids occur under the skin around the anus. The presence of hemorrhoids can be a source of discomfort and embarrassment for many individuals, yet they are a common condition that affects a significant portion of the population at some point in their lives. Understanding the nature of hemorrhoids is crucial for effective management and prevention.
Causes of Hemorrhoids
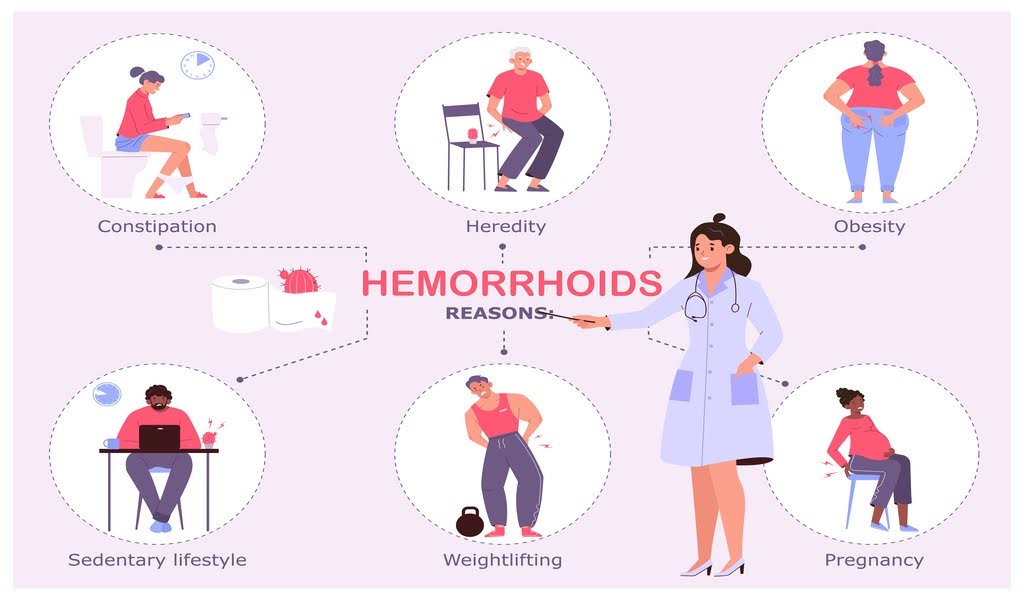
The development of hemorrhoids is often linked to increased pressure in the lower rectum. Several factors can contribute to this pressure:
Straining during bowel movements: This is one of the most common causes, often due to constipation.
Prolonged sitting: Spending long periods on the toilet can increase pressure on the anal veins.
Obesity: Excess body weight can contribute to increased pressure in the rectum.
Pregnancy: The added weight and hormonal changes can lead to the development of hemorrhoids.
Age: As people age, the tissues that support the veins in the rectum can weaken.
In addition to these factors, a diet low in fiber can exacerbate the issue, leading to constipation and straining. Individuals who consume a diet rich in processed foods may find themselves more susceptible to hemorrhoids due to inadequate fiber intake.
Furthermore, heavy lifting and certain medical conditions, such as chronic cough or diarrhea, can also increase the risk of developing hemorrhoids by placing additional strain on the rectum.
Symptoms of Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids can manifest with a variety of symptoms, including:
Pain or discomfort, especially during bowel movements
Itching or irritation in the anal region
Swelling around the anus
Bright red blood on toilet paper or in the toilet bowl
While hemorrhoids can be uncomfortable, they are generally not life-threatening and can often be managed with lifestyle changes and over-the-counter treatments.
However, it is important to note that not all anal bleeding is caused by hemorrhoids; conditions such as anal fissures or even more serious issues like colorectal cancer can also present with similar symptoms.
Therefore, anyone experiencing significant pain or persistent bleeding should seek medical advice for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Additionally, incorporating regular exercise and staying hydrated can significantly improve bowel health and reduce the likelihood of hemorrhoid development.
Understanding Anal Fissures
Anal fissures are small tears in the lining of the anus, which can cause significant pain and discomfort during bowel movements. They often occur in conjunction with constipation or diarrhea, leading to a cycle of pain and avoidance of bowel movements. This condition can affect individuals of all ages, though it is particularly common in infants and adults aged 30 to 60. The experience of an anal fissure can be distressing, as the fear of pain can lead to further complications, such as chronic constipation or even the development of anal abscesses.
Causes of Anal Fissures
Several factors can lead to the development of anal fissures:
Hard stools: Straining to pass hard stools can create tears in the anal lining.
Chronic diarrhea: Frequent bowel movements can irritate and damage the anal area.
Childbirth: Women may experience fissures during or after childbirth due to the stretching of the anal area.
Inflammatory bowel disease: Conditions like Crohn's disease can increase the risk of fissures.
In addition to these factors, lifestyle choices such as a low-fiber diet can contribute significantly to the occurrence of anal fissures. A diet lacking fiber can lead to constipation, making bowel movements more difficult and painful.
Furthermore, certain medications, particularly those that cause constipation as a side effect, can also play a role in the development of fissures. Understanding these causes can help individuals take preventive measures to avoid this painful condition.
Symptoms of Anal Fissures
Anal fissures can present with distinct symptoms, including:
Sharp pain during and after bowel movements
Bleeding, which may appear as bright red blood on the toilet paper
Itching or irritation around the anus
A visible tear or crack in the skin around the anus
The pain associated with anal fissures can be severe, often leading to a fear of bowel movements, which can exacerbate the condition. In some cases, patients may also experience a spasm of the anal sphincter, which can further intensify the discomfort. This cycle of pain and avoidance can lead to a state of anxiety surrounding bowel movements, making it crucial for individuals to seek appropriate treatment. It’s important to note that while anal fissures can be extremely painful, they are often treatable with conservative measures such as dietary changes, topical treatments, and in some cases, surgical options. Early intervention can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing, allowing individuals to regain their comfort and quality of life.
Comparing Hemorrhoids and Anal Fissures
While hemorrhoids and anal fissures share some symptoms, they are distinct conditions with different underlying causes and treatment approaches. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective management.
Key Differences
Location
Main Cause
Pain Level
Hemorrhoids: Varies; may be mild to moderate
Anal Fissures: Severe, especially during bowel movements
Bleeding
Hemorrhoids: Bright red blood, often on toilet paper
Anal Fissures: Bright red blood, typically during bowel movements
Diagnosis
Proper diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Healthcare providers may perform a physical examination and may use additional diagnostic tools such as:
In some cases, a referral to a specialist may be necessary for further evaluation and treatment.
In addition to these diagnostic methods, healthcare providers may also consider a patient's medical history and lifestyle factors that could contribute to the development of these conditions.
For instance, chronic constipation or diarrhea, a low-fiber diet, and sedentary lifestyle are common risk factors for both hemorrhoids and anal fissures. Understanding these contributing factors can help in formulating a comprehensive treatment plan that not only addresses the immediate symptoms but also aims to prevent recurrence.
Furthermore, patient education plays a vital role in managing these conditions. Individuals experiencing symptoms should be encouraged to maintain proper hydration, consume a high-fiber diet, and engage in regular physical activity, as these lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of developing hemorrhoids or anal fissures.
Additionally, knowing when to seek medical attention is crucial; persistent pain, excessive bleeding, or changes in bowel habits should prompt a consultation with a healthcare provider to rule out more serious underlying issues.
Treatment Options for Hemorrhoids
Management of hemorrhoids often begins with conservative measures, but more severe cases may require medical intervention. Here are common treatment options:
Conservative Treatments
Dietary changes: Increasing fiber intake can help soften stools and reduce straining.
Hydration: Drinking plenty of water can aid digestion and prevent constipation.
Over-the-counter medications: Creams and ointments can provide relief from pain and itching.
In addition to these conservative treatments, lifestyle modifications can also play a crucial role in managing hemorrhoids. Regular exercise can improve bowel function and reduce the risk of constipation, while avoiding prolonged sitting or standing can alleviate pressure on the rectum.
Furthermore, establishing a regular bathroom routine, such as not delaying the urge to have a bowel movement, can help prevent the worsening of hemorrhoids. Many individuals find that incorporating gentle yoga or stretching can also relieve discomfort and promote overall digestive health.
Medical Treatments
If conservative measures fail, medical treatments may be necessary:
Rubber band ligation: A procedure that involves placing a band around the base of an internal hemorrhoid to cut off its blood supply.
Sclerotherapy: Involves injecting a solution into the hemorrhoid to shrink it.
Hemorrhoidectomy: Surgical removal of hemorrhoids may be required for severe cases.
Each of these medical treatments has its own set of benefits and potential side effects, which should be discussed with a healthcare provider. For instance, rubber band ligation is a minimally invasive option that can often be performed in an outpatient setting, allowing for a quick recovery.
On the other hand, a hemorrhoidectomy, while effective for larger or more persistent hemorrhoids, may require a longer recovery period and comes with a higher risk of complications. Patients should also be aware of post-treatment care, which may include pain management strategies and follow-up appointments to monitor healing and prevent recurrence.
Treatment Options for Anal Fissures
Similar to hemorrhoids, treatment for anal fissures often starts with conservative measures. Here are some effective strategies:
Conservative Management
High-fiber diet: Incorporating more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help prevent constipation.
Sitz baths: Soaking in warm water can relieve pain and promote healing.
Topical treatments: Creams containing nitroglycerin or calcium channel blockers can help relax the anal sphincter and promote healing.
Medical Interventions
For fissures that do not respond to conservative treatment, medical interventions may be necessary:
Botulinum toxin injections: This can help relax the anal sphincter and promote healing.
Surgery: In severe cases, a surgical procedure called lateral internal sphincterotomy may be performed to relieve tension in the anal sphincter.
In addition to these treatment options, patients are encouraged to maintain a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise. Physical activity can help stimulate bowel function and reduce the risk of constipation, which is a significant contributor to the development of anal fissures. Engaging in activities such as walking, swimming, or yoga can be beneficial not only for digestive health but also for overall well-being.
Furthermore, staying well-hydrated is crucial; drinking plenty of water aids in softening stool and making bowel movements less painful.
It is also important for patients to be aware of the potential for recurrence after treatment. Following a successful intervention, individuals should continue to monitor their diet and lifestyle choices to prevent future fissures. Some may find it helpful to keep a food diary to identify any dietary triggers that may lead to constipation or straining during bowel movements.
Additionally, consulting with a healthcare provider for personalized advice can further enhance recovery and help maintain long-term anal health.
Preventive Measures
Both hemorrhoids and anal fissures can often be prevented through lifestyle modifications. Here are some effective strategies:
Dietary Recommendations
Healthy Bowel Habits
Avoid prolonged sitting on the toilet, which can increase pressure on the anal veins.
Respond to the urge to have a bowel movement promptly to prevent constipation.
Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity can help maintain healthy bowel function and reduce the risk of constipation. Simple exercises like walking or yoga can be beneficial.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While hemorrhoids and anal fissures can often be managed at home, there are instances when medical attention is necessary:
Signs to Watch For
Severe pain that does not improve with home treatment
Persistent bleeding that does not stop
Signs of infection, such as fever or pus
Is It Hemorrhoids or a Fissure? Know for Sure with Doctronic
Hemorrhoids and anal fissures are two common causes of anal pain, each with distinct causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Understanding the differences can aid in effective management and prevention. Individuals experiencing symptoms should consider lifestyle changes and consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. With the right approach, both conditions can be effectively managed, leading to relief and improved quality of life.
Take control of your health with Doctronic today! Understanding the difference between hemorrhoids and fissures is the first step to finding relief. Learn how to identify your symptoms, address the root cause, and reclaim your comfort—because you deserve to feel your best every day!




