Skin rashes can be perplexing, especially when they arise suddenly and without warning. Two common conditions that often lead to confusion are folliculitis and herpes. While both can cause discomfort and concern, understanding their differences is crucial for effective treatment and management. This article delves into the characteristics, causes, symptoms, and treatment options for folliculitis and herpes, helping to clarify the distinctions between these two skin conditions.
 Understanding Folliculitis
Understanding Folliculitis
Folliculitis is an inflammatory condition affecting the hair follicles. It can occur anywhere on the body where hair is present, including the scalp, face, arms, and legs. This condition is often characterized by small red bumps or pustules that can be itchy or painful. While folliculitis is generally not a serious health threat, it can be uncomfortable and may lead to secondary infections if not managed properly. Understanding the nuances of this condition can help individuals take proactive measures to prevent and treat it effectively.
Causes of Folliculitis
The causes of folliculitis can vary widely, but some of the most common include:
Bacterial Infection: The most common cause is a bacterial infection, particularly from Staphylococcus aureus.
Fungal Infection: Fungi can also cause folliculitis, especially in warm, moist environments.
Ingrown Hairs: Shaving or waxing can lead to ingrown hairs, which may become inflamed.
Occlusive Clothing: Tight clothing can trap sweat and bacteria, increasing the risk of folliculitis.
Additionally, certain lifestyle factors can exacerbate the condition. For instance, individuals who frequently engage in activities that cause excessive sweating, such as exercising or working in hot environments, may find themselves more susceptible to folliculitis.
Furthermore, those with compromised immune systems or underlying skin conditions, such as eczema or acne, may also experience more frequent flare-ups. Understanding these risk factors can empower individuals to make informed choices about their skin care and hygiene practices.
Symptoms of Folliculitis
Folliculitis manifests in several ways, including:
Red, inflamed bumps around hair follicles
Pustules that may ooze or crust over
Itching or tenderness in the affected area
In more severe cases, folliculitis can lead to larger, painful boils or abscesses that require medical attention. The symptoms can vary in intensity, with some individuals experiencing mild irritation while others may endure significant discomfort. It is also important to note that folliculitis can sometimes resemble other skin conditions, such as acne or dermatitis, making an accurate diagnosis crucial. If left untreated, persistent folliculitis can lead to scarring or changes in skin pigmentation, which may be distressing for those affected. Regular monitoring of the skin and seeking medical advice when symptoms arise can help mitigate these risks and promote healthier skin overall.
Understanding Herpes
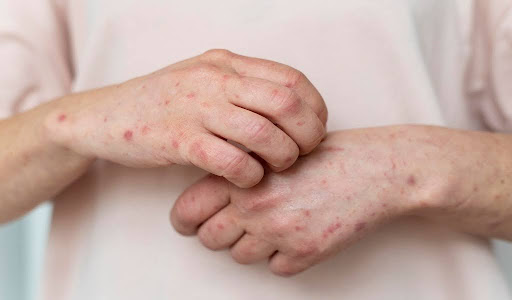 Herpes is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), which is categorized into two types: HSV-1 and HSV-2. HSV-1 typically causes oral herpes, while HSV-2 is primarily associated with genital herpes. Both types can lead to painful blisters and sores. The prevalence of herpes is significant, with millions of people worldwide affected by this virus, making it one of the most common sexually transmitted infections. Despite its widespread nature, there remains a considerable stigma surrounding the condition, often leading to feelings of shame and isolation for those diagnosed.
Herpes is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), which is categorized into two types: HSV-1 and HSV-2. HSV-1 typically causes oral herpes, while HSV-2 is primarily associated with genital herpes. Both types can lead to painful blisters and sores. The prevalence of herpes is significant, with millions of people worldwide affected by this virus, making it one of the most common sexually transmitted infections. Despite its widespread nature, there remains a considerable stigma surrounding the condition, often leading to feelings of shame and isolation for those diagnosed.
Causes of Herpes
Herpes is highly contagious and can be transmitted through direct contact with an infected person. Key transmission methods include:
Skin-to-Skin Contact: Engaging in intimate activities with an infected person can lead to transmission.
Oral Contact: Sharing utensils, lip balms, or engaging in oral sex can spread the virus.
Asymptomatic Shedding: The virus can be transmitted even when sores are not present.
Additionally, it is important to note that the virus can survive on surfaces for a limited time, which means that indirect transmission, although less common, is still a possibility. Individuals who are asymptomatic can unknowingly spread the virus, which underscores the importance of open communication about sexual health and regular testing for sexually active individuals.
Symptoms of Herpes
Herpes symptoms can vary, but common signs include:
Painful blisters or sores on the mouth, genitals, or surrounding areas
Itching or burning sensations prior to the appearance of blisters
Flu-like symptoms, such as fever and swollen lymph nodes, during the initial outbreak
After the initial outbreak, the virus remains dormant in the body and can reactivate, leading to recurrent episodes. The frequency and severity of these outbreaks can differ greatly among individuals, with some experiencing frequent recurrences while others may have infrequent or mild episodes. Stress, illness, and hormonal changes are known triggers for reactivation, highlighting the need for individuals to manage their overall health and well-being to potentially reduce the frequency of outbreaks.
Comparing Folliculitis and Herpes
While both folliculitis and herpes can cause skin rashes, there are distinct differences that set them apart. Understanding these differences can aid in proper diagnosis and treatment.
Key Differences
Cause
Appearance
Location
Contagiousness
Treatment
Folliculitis often arises due to irritation from shaving, friction from clothing, or occlusion from oils and lotions, making it a common concern for individuals with sensitive skin or those who frequently engage in activities that cause skin trauma. The condition can manifest as small, itchy bumps that may become crusty if scratched.
If left untreated, folliculitis can lead to more severe infections, resulting in deeper skin issues or even scarring. Maintaining proper hygiene and avoiding tight clothing can help prevent folliculitis, as can using non-comedogenic products that do not clog pores.
On the other hand, herpes is characterized by its recurrent nature, with outbreaks often triggered by stress, illness, or sun exposure. The initial infection may present flu-like symptoms, including fever and swollen lymph nodes, before the appearance of blisters. Once contracted, the herpes virus remains dormant in the body, leading to periodic flare-ups that can be distressing for those affected. Education about transmission and safe practices is crucial in managing herpes, as individuals may unknowingly spread the virus even when asymptomatic. Understanding the emotional and psychological impacts of living with herpes is also vital, as stigma can affect mental health and relationships.
Diagnosis: How Are They Differentiated?
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Healthcare professionals typically rely on a combination of patient history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Understanding the nuances of each condition is crucial, as misdiagnosis can lead to inappropriate treatments and prolonged discomfort for the patient.
Physical Examination
A thorough physical examination can often reveal the nature of the rash. Folliculitis typically presents as clusters of red bumps around hair follicles, while herpes shows distinct blisters or sores. The location of the rash can also provide clues; for instance, genital sores are more indicative of herpes.
Additionally, the presence of symptoms such as itching, pain, or fever can further assist in narrowing down the diagnosis. For instance, folliculitis may be accompanied by itching, while herpes lesions are often painful and may be preceded by a tingling sensation in the affected area.
Laboratory Tests
In some cases, laboratory tests may be necessary to confirm a diagnosis. These tests can include:
Culture Test: A sample from the lesion can be cultured to identify the specific pathogen.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): This test can detect the genetic material of the herpes virus.
Blood Tests: Blood tests can determine if a person has been exposed to the herpes virus.
In addition to these tests, healthcare providers may also consider serological tests that measure the immune response to the herpes virus. These tests can help differentiate between HSV-1 and HSV-2, which is important for understanding the potential risks and implications of the infection.
Moreover, rapid testing methods are becoming increasingly available, allowing for quicker diagnosis and treatment initiation, which can significantly improve patient outcomes. The choice of tests often depends on the clinical presentation and the healthcare provider's judgment, ensuring that the most appropriate diagnostic approach is taken for each individual case.
Treatment Options
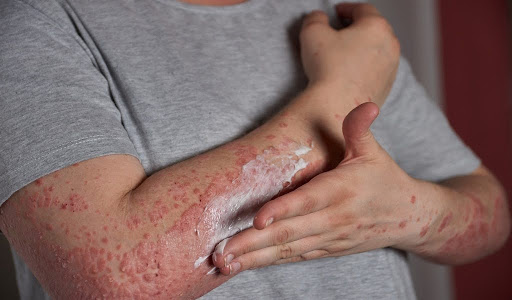 Effective treatment varies significantly between folliculitis and herpes, reflecting their different causes and symptoms.
Effective treatment varies significantly between folliculitis and herpes, reflecting their different causes and symptoms.
Treatment for Folliculitis
Folliculitis is often manageable with home care and over-the-counter treatments. Options include:
Topical Antibiotics: Creams or ointments containing antibiotics can help clear bacterial infections.
Antifungal Treatments: For fungal folliculitis, antifungal creams may be prescribed.
Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses can soothe inflammation and promote healing.
In severe cases, oral antibiotics or antifungals may be necessary. Preventive measures, such as avoiding tight clothing and practicing good hygiene, can also help reduce the risk of recurrence.
Additionally, maintaining a healthy skin care routine is crucial; gentle cleansing and moisturizing can support skin health and prevent irritation that may lead to folliculitis. For those prone to recurrent outbreaks, dermatologists may recommend laser hair removal or other hair removal techniques that minimize irritation to the hair follicles.
Treatment for Herpes
Herpes management focuses on reducing symptoms and preventing outbreaks. Treatment options include:
Antiviral Medications: Drugs like acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir can help manage outbreaks and reduce transmission risk.
Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers can alleviate discomfort associated with sores.
Topical Treatments: Creams may provide temporary relief from itching and discomfort.
While there is no cure for herpes, many individuals find that with proper management, they can lead healthy, fulfilling lives. Education about the condition is also vital; understanding triggers such as stress, illness, or hormonal changes can empower individuals to take proactive steps in managing their health.
Furthermore, open communication with partners about the condition can foster understanding and reduce anxiety surrounding outbreaks, ultimately leading to a more supportive and informed relationship.
Preventive Measures
Taking preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of both folliculitis and herpes.
Preventing Folliculitis
To minimize the chances of developing folliculitis, consider the following tips:
Practice good hygiene by regularly cleansing the skin.
Avoid sharing personal items, such as razors and towels.
Wear loose-fitting clothing to reduce friction and irritation.
Use clean, sharp razors when shaving and shave in the direction of hair growth.
Preventing Herpes
To lower the risk of herpes transmission, individuals can take several precautions:
Engage in safe sexual practices, including the use of condoms.
Avoid intimate contact during an active outbreak.
Communicate openly with partners about your herpes status.
Consider antiviral medication if you frequently experience outbreaks.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While both conditions can often be managed at home, there are circumstances where medical attention is necessary.
Signs to Watch For
Individuals should seek medical advice if they experience:
Severe pain or discomfort
Fever or systemic symptoms accompanying the rash
Rash that worsens or does not improve with home treatment
Frequent recurrences of either condition
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Consulting a healthcare professional can provide clarity and peace of mind. They can offer tailored advice, perform necessary tests, and prescribe appropriate treatments based on individual needs.
Still Unsure? Ask Doctronic About Your Skin Concerns
Understanding the differences between folliculitis and herpes is vital for effective management and treatment. While both conditions can cause skin rashes, their causes, symptoms, and treatments differ significantly. By recognizing the signs and seeking appropriate care, individuals can navigate these skin issues more effectively and maintain their overall health. Whether dealing with folliculitis or herpes, informed decisions and proactive measures can lead to better outcomes and improved quality of life.
Don’t let uncertainty hold you back from taking control of your health! Doctronic will help you understand whether a rash is folliculitis or herpes, which can make all the difference in getting the right care. Empower yourself with knowledge—consult a healthcare provider today and take the first step toward relief and confidence.



 Understanding Folliculitis
Understanding Folliculitis Herpes is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), which is categorized into two types: HSV-1 and HSV-2. HSV-1 typically causes oral herpes, while HSV-2 is primarily associated with genital herpes. Both types can lead to painful blisters and sores. The prevalence of herpes is significant, with millions of people worldwide affected by this virus, making it one of the most common sexually transmitted infections. Despite its widespread nature, there remains a considerable stigma surrounding the condition, often leading to feelings of shame and isolation for those diagnosed.
Herpes is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), which is categorized into two types: HSV-1 and HSV-2. HSV-1 typically causes oral herpes, while HSV-2 is primarily associated with genital herpes. Both types can lead to painful blisters and sores. The prevalence of herpes is significant, with millions of people worldwide affected by this virus, making it one of the most common sexually transmitted infections. Despite its widespread nature, there remains a considerable stigma surrounding the condition, often leading to feelings of shame and isolation for those diagnosed. Effective treatment varies significantly between folliculitis and herpes, reflecting their different causes and symptoms.
Effective treatment varies significantly between folliculitis and herpes, reflecting their different causes and symptoms.