Eczema vs Scabies: How to Identify and Treat Each
Distinguishing Eczema and Scabies: What You Need to KnowWhen it comes to itchy skin conditions, eczema and scabies often get confused. Both cause discomfort and visible skin [...]
Read More
Medically reviewed by Alan Lucks | MD, Alan Lucks MDPC Private Practice - New York on December 19th, 2025.
Understand the key differences between eczema and scabies in symptoms and causes
Learn how to identify each condition through common signs and diagnostic tips
Explore effective treatment options, including when to seek professional care
Discover how telehealth services like Doctronic.ai can help with diagnosis and ongoing management
Get answers to frequently asked questions about eczema and scabies
When it comes to itchy skin conditions, eczema and scabies often get confused. Both cause discomfort and visible skin changes, but they have very different origins and treatments. Knowing how to tell them apart can save you time, reduce frustration, and ensure you get the right care quickly.
Eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions worldwide. It causes dry, red, and itchy patches that can flare up due to triggers like allergens or irritants. Scabies, on the other hand, is an infectious condition caused by tiny mites burrowing into the skin. It spreads through close contact and requires specific treatment to eliminate the mites.
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, arises from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. It is not contagious. The skin’s barrier function is impaired, making it prone to dryness and irritation. Common triggers include soaps, detergents, stress, temperature changes, and allergens like pollen or pet dander. In addition to these triggers, certain lifestyle factors can exacerbate eczema symptoms. For instance, excessive bathing or using hot water can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to further dryness and irritation. Emotional stress has been shown to play a significant role in flare-ups, as it can trigger the release of inflammatory substances in the body, worsening the condition.
Scabies is caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite. These microscopic parasites burrow into the upper layer of the skin to lay eggs, triggering intense itching and rash. Scabies spreads easily through prolonged skin-to-skin contact and can affect people of all ages and backgrounds. The symptoms often manifest as small, red bumps or blisters, typically found in the webbing of fingers, wrists, and other warm areas of the body. It's important to note that scabies can also be contracted through sharing personal items like towels or bedding, making it a concern in crowded living conditions. The itching associated with scabies can become more severe at night, leading to significant discomfort and sleep disturbances, which can further impact a person's overall well-being.
Itching: Often intense, especially at night
Appearance: Dry, scaly, red patches that may crack or ooze
Common Locations: Inside elbows, between fingers, behind knees, face, neck, and hands
Chronic Pattern: Symptoms can flare and subside over time
Eczema patches vary in size and shape. The skin may become thickened after repeated scratching. Unlike scabies, eczema does not cause burrow marks or tiny raised lines on the skin. It is important to note that eczema is often linked to environmental factors and allergies, which can exacerbate symptoms. Common triggers include certain fabrics, soaps, and even temperature changes. Individuals with eczema may also experience dry skin, which can lead to further irritation and discomfort if not properly managed.
In addition to the physical symptoms, eczema can have a significant emotional impact on those affected. Many individuals, especially children, may feel self-conscious about their skin condition, leading to anxiety or social withdrawal. Managing eczema often involves a comprehensive approach that includes moisturizing regularly, using topical corticosteroids, and sometimes incorporating antihistamines to alleviate itching. Understanding the triggers and maintaining a consistent skincare routine can greatly improve the quality of life for those living with eczema.
Itching: Severe and often worse at night
Rash: Small red bumps, blisters, or pimple-like irritations
Burrows: Thin, irregular tracks made by mites under the skin, often found between fingers, wrists, waistline, and genital area
Spread: Rash often appears in multiple areas due to mite migration
Scabies can sometimes cause crusted or Norwegian scabies, a severe form with thick crusts and widespread skin involvement, especially in people with weakened immune systems. This variant is highly contagious and can spread rapidly in environments such as nursing homes or among individuals with close physical contact. The intense itching associated with scabies can lead to secondary bacterial infections, as the skin becomes compromised from scratching.
Diagnosis of scabies typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare professional, who may take skin scrapings to confirm the presence of mites or their eggs. Treatment usually includes prescription topical medications that kill the mites, and it is crucial for all close contacts to be treated simultaneously to prevent re-infestation. Laundering bedding and clothing in hot water is essential to eliminate any lingering mites. Understanding scabies and its transmission can help reduce stigma and promote effective treatment and prevention strategies within communities.
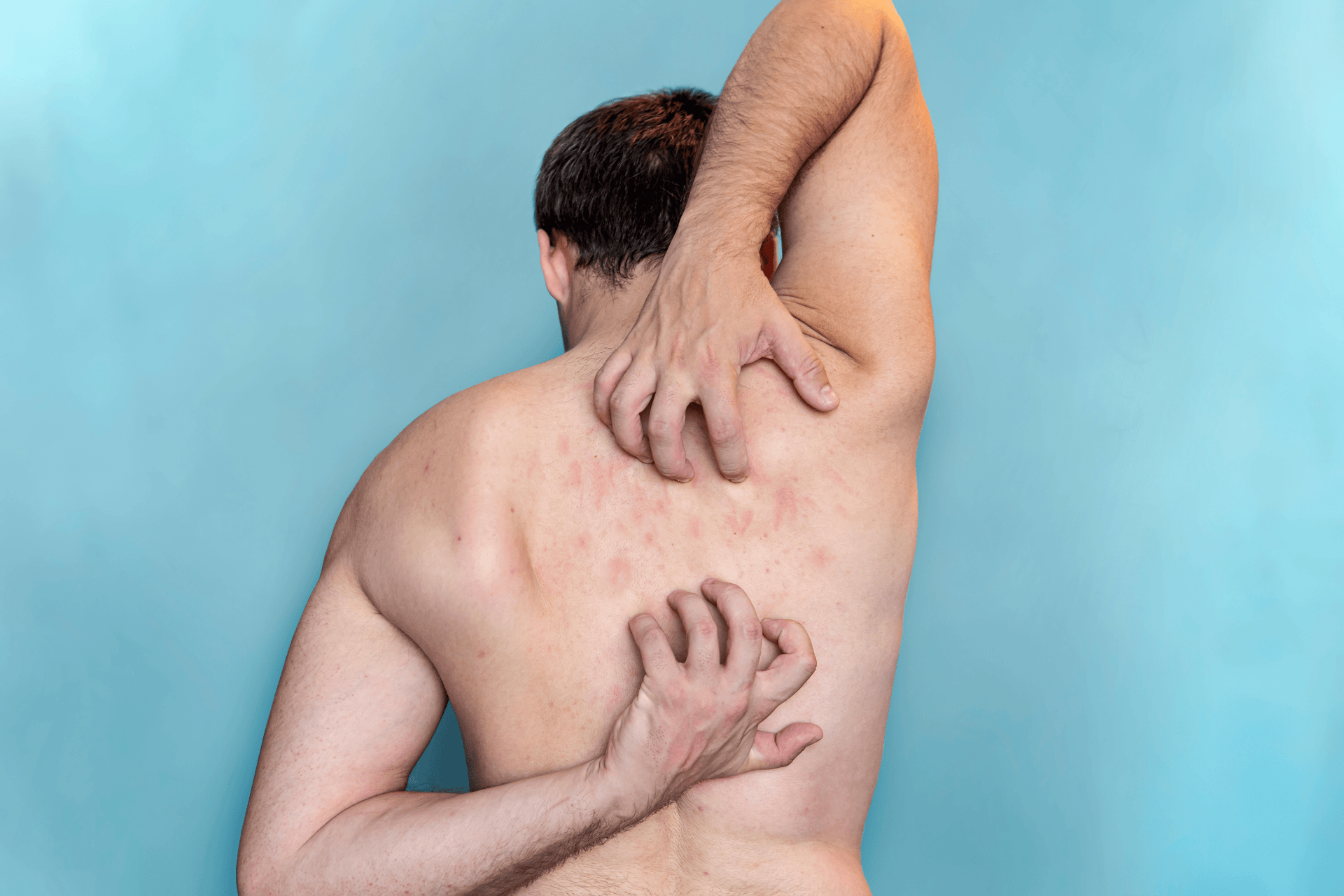 Diagnosing Eczema and Scabies: What to Expect
Diagnosing Eczema and Scabies: What to ExpectDiagnosis of eczema is primarily clinical, based on the appearance of the skin and patient history. Doctors look for typical signs such as dry, itchy patches and may ask about family history of allergies or asthma. Sometimes, patch testing is done to identify specific allergens that trigger eczema.
Scabies diagnosis involves identifying the characteristic burrows and rash. A doctor may perform a skin scraping to examine under a microscope for mites, eggs, or fecal matter. Because scabies spreads easily, doctors often recommend treating close contacts simultaneously.
If you notice persistent itching and rash but are unsure of the cause, telehealth services like Doctronic.ai offer a convenient way to get a professional evaluation quickly. You can describe your symptoms, share photos, and receive guidance without leaving home. For non-emergency skin concerns, this can speed up diagnosis and treatment.
Moisturizing: Regular use of emollients to restore the skin barrier
Topical Steroids: To reduce inflammation during flare-ups
Avoid Triggers: Identifying and minimizing exposure to irritants
Antihistamines: Sometimes used to reduce itching
Advanced Therapies: For severe cases, doctors may prescribe immunomodulators or biologics
Consistency is key in eczema care. Keeping skin hydrated and avoiding scratching can prevent worsening symptoms. If over-the-counter treatments fail, consulting a healthcare provider is important.
Prescription Creams: Permethrin cream is the most common treatment
Oral Medications: Ivermectin may be prescribed for difficult cases
Cleaning Environment: Washing bedding, clothing, and vacuuming to remove mites
Treating Contacts: Family members and close contacts should be treated simultaneously
Itching may persist for several weeks after treatment as the skin heals, but the mites will be eliminated. If symptoms continue or worsen, follow-up with a healthcare provider is necessary.
Getting timely, accurate advice for skin conditions can be challenging. Doctronic.ai offers free AI-powered doctor visits that provide fast, evidence-based answers drawing on the latest medical research. Whether you suspect eczema or scabies, you can get a detailed assessment online and decide on the next steps.
For more personalized care, Doctronic also provides affordable telehealth video visits with licensed doctors 24/7 across all 50 states. This means you can discuss your symptoms in depth, receive prescriptions if needed, and manage follow-up care without leaving your home.
With over 10 million users benefiting from Doctronic’s AI-driven approach, it’s a trusted tool for primary care powered by modern medicine. Visit Doctronic.ai to start your consultation today.
Both eczema and scabies cause itching and visible skin changes, but their causes and treatments differ significantly. Recognizing the signs of each condition helps you take the right steps toward relief. Persistent or severe symptoms always warrant professional evaluation.
Telehealth platforms like Doctronic.ai make it easier than ever to access expert care quickly. With AI-driven insights and real doctors available anytime, managing your skin health is more convenient and personalized.
No, eczema is not contagious and cannot turn into scabies. Scabies is caused by mites and requires direct contact for transmission.
Itching can continue for 2 to 4 weeks after successful treatment as the skin recovers, but the mites are no longer active.
Eczema often runs in families and is linked to genetic factors affecting skin barrier function and immune response.
Scabies requires prescription medication to eliminate mites. Home remedies are not effective and may delay proper treatment.
If symptoms are severe, spreading, or not improving with over-the-counter treatments, seek medical advice. Telehealth services like Doctronic.ai can provide rapid evaluation and treatment recommendations.
Distinguishing Eczema and Scabies: What You Need to KnowWhen it comes to itchy skin conditions, eczema and scabies often get confused. Both cause discomfort and visible skin [...]
Read More