Menopause Mood Swings
Menopause brings profound hormonal shifts extending far beyond hot flashes and irregular periods. As estrogen and progesterone levels decline, many women experience [...]
Read More
Medically reviewed by Jerome Albert Ecker | MD, Assistant Professor of Medicine, Duke University - Durham, NC on July 17th, 2023.
These disorders fall into two main categories: inherited conditions like Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (affecting 1 in 5,000 people) and autoimmune diseases like lupus, which strikes 1.5 million Americans, predominantly women aged 15-45.
Joint pain affects over 95% of patients and typically appears symmetrically (both hands, both knees), while skin manifestations range from the butterfly rash of lupus to hyperelastic skin that stretches beyond normal limits.
Antinuclear antibody (ANA) tests are positive in 98% of lupus cases, while genetic testing can identify specific mutations in collagen genes for inherited forms like osteogenesis imperfecta.
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) like methotrexate can slow autoimmune progression when started within 6 months of symptom onset, significantly improving long-term outcomes.
Physical therapy focusing on low-impact exercises and joint protection techniques can maintain mobility for years, while avoiding high-contact sports prevents joint damage in hypermobile patients.
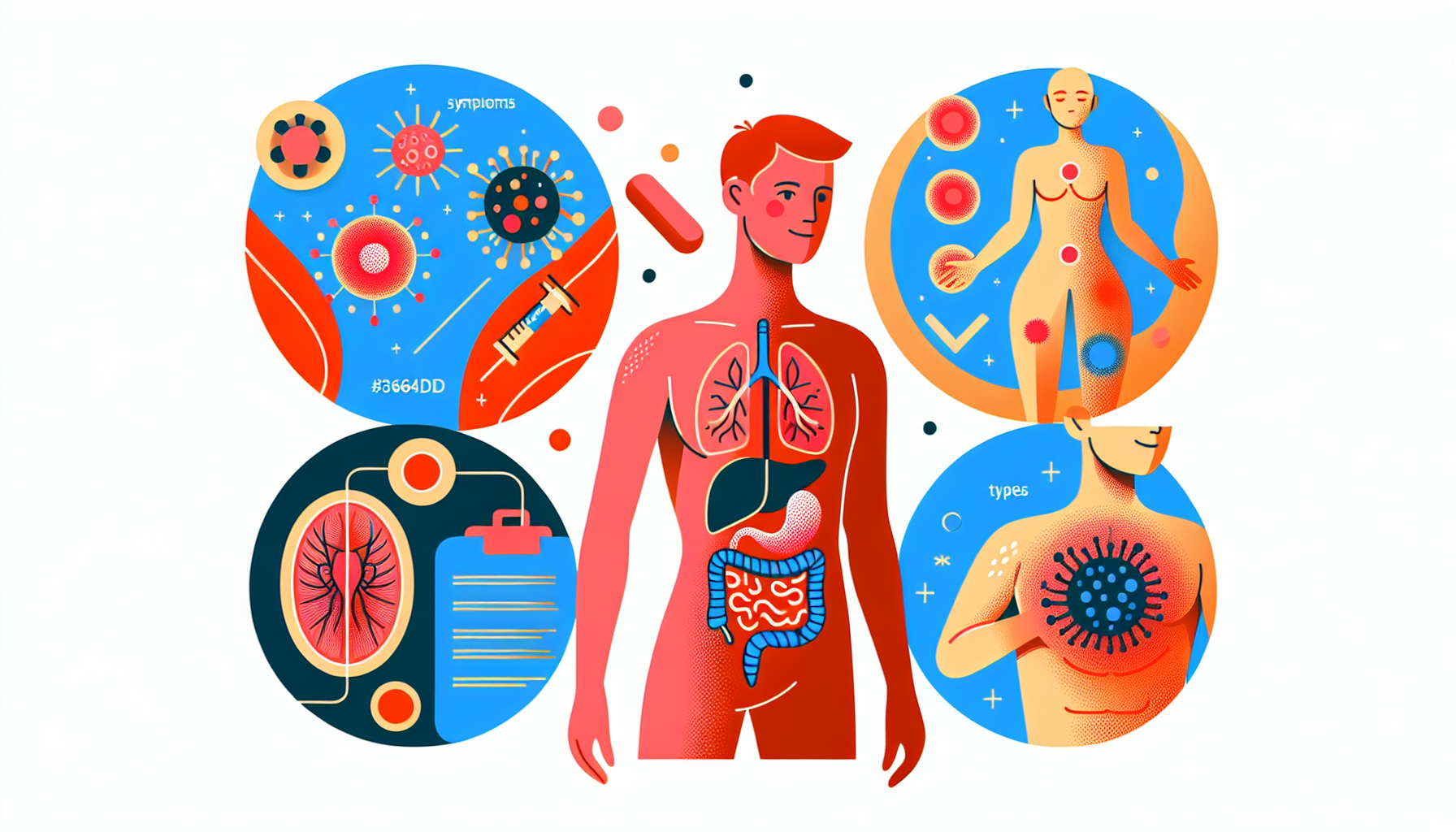
Connective tissue diseases are a group of disorders that affect the protein-rich tissue supporting various parts of the body, such as fat, bone, and cartilage. These conditions can cause a wide range of symptoms and may affect the joints, muscles, skin, bones, internal organs such as the heart, lungs, and digestive tract, as well as the brain. In this article, we'll explore the different types of connective tissue diseases, their symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
There are two main categories of connective tissue diseases: inherited disorders and autoimmune diseases.
Inherited disorders of connective tissue (HDCTs) are caused by genetic changes and are often rare. Some common examples include:
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS)
Epidermolysis bullosa (EB)
Marfan syndrome
Osteogenesis imperfecta
Autoimmune diseases occur when the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues. The exact cause is unknown, but researchers believe that a combination of genetic susceptibility and environmental triggers may play a role. Some examples of autoimmune connective tissue diseases include:
Polymyositis and dermatomyositis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Scleroderma
Sjogren's syndrome
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE or lupus)
Vasculitis
Mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD)
Symptoms of connective tissue diseases can vary depending on the specific condition and the parts of the body affected. Some common symptoms include:
Joint pain, stiffness, and swelling
Muscle weakness and pain
Skin rashes, tightness, or fragility
Fatigue
Fever
Digestive problems
Breathing difficulties
Diagnosing connective tissue diseases often involves a combination of physical examinations, blood tests, imaging studies, and sometimes biopsies. Treatment options vary depending on the specific condition but may include:
Medications to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms
Physical therapy to improve joint function and muscle strength
Occupational therapy to help with daily activities
Surgery to correct joint deformities or address organ damage
If you suspect that you or a loved one may have a connective tissue disease, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. With proper management and care, many people with connective tissue diseases can lead full and active lives.
For more information on connective tissue diseases, visit:
Early diagnosis within the first year of symptoms dramatically improves treatment effectiveness, especially for autoimmune variants that respond well to modern immunosuppressive therapies. The key is recognizing patterns like symmetric joint involvement, distinctive rashes, or unusual skin elasticity that distinguish these conditions from common arthritis. If you're experiencing persistent joint pain with skin changes or family history of connective tissue disorders, Doctronic can help you understand your symptoms and guide next steps.
Menopause brings profound hormonal shifts extending far beyond hot flashes and irregular periods. As estrogen and progesterone levels decline, many women experience [...]
Read MoreLower back pain affects millions of people daily, whether from sitting too long at a desk, lifting heavy objects, or dealing with chronic conditions. While what causes lower [...]
Read MoreThe liver stands as one of your body's most hardworking organs, performing over 500 vital functions from detoxification to protein production. Yet liver disease often [...]
Read More